Megatron源码解读(不再着重理论分析,针对代码细节解读)
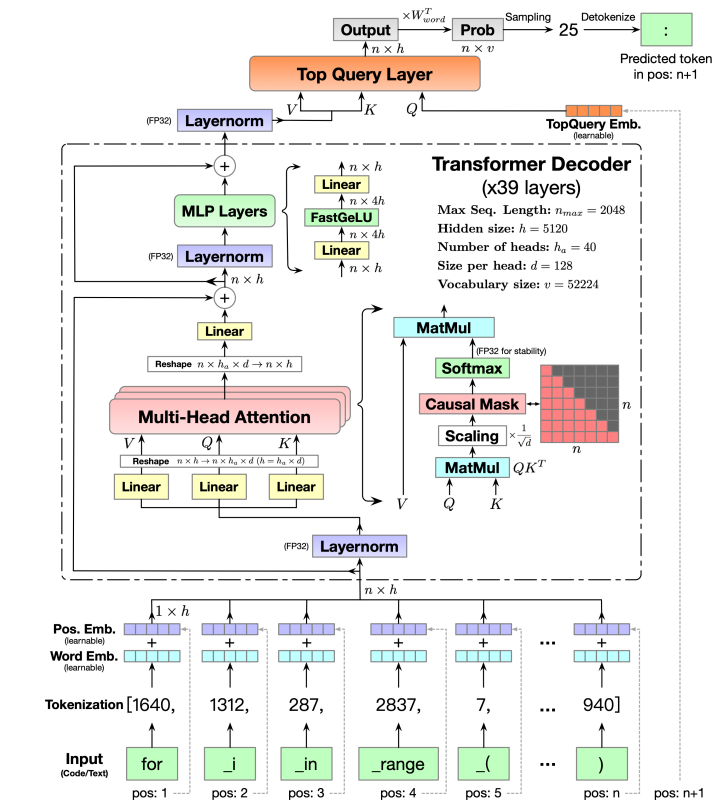
这里放置了一个CodeGeeX模型的结构图,可以看到这里采用的是与GPT类似的Only-Decoder的架构,以CodeGeeX模型为基础研究源码,codegeex采用的是8头TP,192头DP,共1536块GPU进行训练,采用的框架是Megatron+DeepSpeed ZeRo2。
1.预训练入口 pretrain_gpt.py
函数调用关系图
主程序入口
└── pretrain()
├── train_valid_test_datasets_provider() → 构建数据集
├── model_provider()
│ ├── CodeGeeXModel / CodeGeeXModelPipe → 构建模型
│ └�── get_batch_pipe (引用) → 管道并行批次处理
└── forward_step()
├── get_batch() → 获取批次数据
├── model() → 模型前向传播
└── loss_func() → 计算损失
1.1model_provider
构建 CodeGeeX 模型实例,使用DeepSpeed ZeRO 初始化,包含非PP的model CodeGeeXModel和PPmodel CodeGeeXModelPipe。构建casual attention mask(下三角矩阵)供训练使用。可以通过model_path加载模型权重。
def model_provider(pre_process=True, post_process=True):
...
with deepspeed.zero.Init(
data_parallel_group=mpu.get_data_parallel_group(),
remote_device=None if args.remote_device == "none" else args.remote_device,
config_dict_or_path=args.deepspeed_config,
enabled=args.zero_stage == 3,
mpu=mpu,
):
attention_mask = torch.tril(
torch.ones(
(1, args.seq_length, args.seq_length),
device=torch.cuda.current_device(),
)
).view(1, 1, args.seq_length, args.seq_length)
# Convert attention mask to binary:
attention_mask = attention_mask < 0.5
if args.fp16:
attention_mask = attention_mask.half()
elif args.bf16:
attention_mask = attention_mask.bfloat16()
# Attention mask must be bool.
args.attn_mask = attention_mask.to(torch.bool)
if args.load_state is not None:
timers = get_timers()
print_rank_0("Loading warmstarting model states ...")
timers("load-model-states").start()
mp_rank = mpu.get_tensor_model_parallel_rank()
if os.path.isdir(args.load_state):
model_path = os.path.join(
args.load_state, "mp_rank_{:02d}_model_states.pt".format(mp_rank)
)
else:
model_path = args.load_state
print_rank_0(f"Loading model from {model_path} ...")
state_dict = torch.load(model_path, map_location="cpu")
if "module" in state_dict:
state_dict = state_dict["module"] # strip other client states
model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
2. get_batch
使用数据迭代器获取一个批次的数据,并且使用broadcast在多进程间广播数据。
def get_batch(data_iterator):
...
if data_iterator is not None:
data = next(data_iterator)
else:
data = None
data_b = mpu.broadcast_data(keys, data, datatype)
tokens_ = data_b["input_ids"].long()
labels = tokens_[:, 1:].contiguous()
tokens = tokens_[:, :-1].contiguous()
attention_mask, loss_mask, position_ids = get_ltor_masks_and_position_ids(
tokens,
tokenizer.eod,
args.reset_position_ids,
args.reset_attention_mask,
args.eod_mask_loss,
)
考虑 EOD(End of Document)标记的处理,来动态生成casual attention mask,因为通常训练时,会将多个句子拼接如下:
位置: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Token: A B C EOD D E F EOD G H
文档: [文档1] [文档2] [文档3]
如果直接用固定的mask,会导致D能看到前面A,B,C即文档1的内容,然后文档之间的数据应该是各自独立的,因此需要根据eod来设置casual attention mask,如下:
注意力掩码:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0 [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
1 [1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
2 [1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
3 [1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] ← EOD
4 [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0] ← D 只能看到自己!
5 [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0] ← E 只能看到 D, E
6 [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0]
7 [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0] ← EOD
8 [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0] ← G 只能看到自己!
9 [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1] ← H 只能看到 G, H
loss_mask则是用来将eod位置的token标记为0,表示不参与loss计算,其它位置的token都标记为1参与运算。
3. get_batch_pipe(data)
在pipeline parallel下使用,直接接收已获取的数据(data),而不是数据迭代器,DeepSpeed PipelineEngine会自动管理数据,从数据迭代器获取数据,并传递给get_batch_pipe。
def get_batch_pipe(data):
...
data_b = mpu.broadcast_data(keys, data, datatype)
# Unpack.
tokens_ = data_b["input_ids"].long()
labels = tokens_[:, 1:].contiguous()
tokens = tokens_[:, :-1].contiguous()
return (tokens, position_ids, attention_mask), (labels, loss_mask)
4. loss_func(loss_mask, output_tensor)
用于计算损失,并且会对dp的loss做reduce。
def loss_func(loss_mask, output_tensor):
losses = output_tensor.float()
loss_mask = loss_mask.view(-1).float()
loss = torch.sum(losses.view(-1) * loss_mask) / loss_mask.sum()
# Reduce loss for logging.
averaged_loss = average_losses_across_data_parallel_group([loss])
return loss, {"lm loss": averaged_loss[0]}
5. forward_step(data_iterator, model)
执行前向传播,返回输出张量和部分应用的损失函数(使用 partial 绑定 loss_mask)
def forward_step(data_iterator, model):
"""Forward step."""
args = get_args()
timers = get_timers()
# Get the batch.
timers("batch-generator").start()
tokens, labels, loss_mask, attention_mask, position_ids = get_batch(data_iterator)
timers("batch-generator").stop()
output_tensor = model(tokens, position_ids, attention_mask, labels=labels)
return output_tensor, partial(loss_func, loss_mask)
6. train_valid_test_datasets_provider(train_val_test_num_samples)
数据集构建:
- 调用
build_train_valid_test_datasets函数:- 使用配置的数据路径、数据实现方式、分割比例等参数
- 设置序列长度、随机种子等
- 控制内存映射预热(mmap_warmup)
- 打印数据集构建进度信息
def train_valid_test_datasets_provider(train_val_test_num_samples):
...
train_ds, valid_ds, test_ds = build_train_valid_test_datasets(
data_prefix=args.data_path,
data_impl=args.data_impl,
splits_string=args.split,
train_valid_test_num_samples=train_val_test_num_samples,
seq_length=args.seq_length,
seed=args.seed,
skip_warmup=(not args.mmap_warmup),
)
7.主程序入口
Megatron-LM预训练的核心入口是pretrain函数。
if __name__ == "__main__":
pretrain(
train_valid_test_datasets_provider,
model_provider,
ModelType.encoder_or_decoder,
forward_step,
args_defaults={'tokenizer_type': 'GPT2BPETokenizer'},
)
8.pretrain函数
def pretrain(
train_valid_test_dataset_provider, # 数据集提��供函数:根据数据集大小返回训练/验证/测试数据集
model_provider, # 模型提供函数:返回一个基础的模型实例(CPU上,无fp16或ddp)
forward_step_func, # 前向传播函数:接收数据迭代器和模型,返回损失值和监控信息字典
valid_forward_step_func=None, # 验证前向传播函数(可选)
extra_args_provider=None, # 额外参数提供函数:用于添加自定义命令行参数
args_defaults={}, # 参数字典:用于设置已解析的参数默认值
):
"""
主训练程序。
此函数将按以下顺序执行:
1) 初始化 Megatron。
2) 使用 model_provider 设置模型、优化器和学习率调度器。
3) 调用 train_val_test_data_provider 获取训练/验证/测试数据集。
4) 使用 forward_step_func 训练模型。
参数说明:
train_valid_test_dataset_provider: 接收训练/验证/测试数据集大小的函数,
返回 `train, valid, test` 数据集。
model_provider: 返回模型基础版本的函数。基础版本指在CPU上的简单模型,
没有fp16或ddp。
forward_step_func: 接收 `数据迭代器` 和 `模型` 的函数,返回一个 `损失` 标量
和一个字典,字典的键值对是我们希望在训练期间监控的信息,例如
`lm-loss: value`。我们还要求此函数将 `batch generator` 添加到计时器类中。
extra_args_provider: 接收解析器并向其添加参数的函数。
用于程序添加自己的参数。
args_defaults: 从参数名到参数值的字典。用于设置已解析的参数。
"""
pretrain 函数是 CodeGeeX 预训练流程的核心协调函数,它按照固定的顺序执行以下任务:
1.初始化megatron框架,加载deepspeed配置,并且构建模型实例,优化器,以及学习率调度器。
2.根据是否使用PP,构建训练、验证、测试的数据
这里主要通过initialize_megatron来初始化megatron的分布式环境,在initialize_megatron中主要调用_initialize_distributed()方法对分布式环境进行初始化,如下:
def _initialize_distributed():
"""Initialize torch.distributed and mpu.
| Node1 | Node2 |
____________| p1 | p2 | p3 | p4 |
local_rank | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
rank | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
node: 物理结点,1台机器或者1个容器。图中2个物理结点
rank:进程在全局上的序号。图中4个进程
local_rank:进程在node上的序号。
torch.cuda.device_count():当前进程所在的node上可使用的GPU的数量
device:GPU在某个node上的编号
该函数作用:
1、设置分布式环境:初始化进程,分配GPU,并设置进程大组(group)
2、制定DP/TP/PP分组策略,设置进程子组(subgroup)
3、设置DeepSpeed ZeRO-R,对activation进行优化
"""
args = get_args()
device_count = torch.cuda.device_count() # 当前进程所在的node上可使用的GPU的数量
if torch.distributed.is_initialized(): # 如果已创建好分布式环境
if args.rank == 0: # 在0号��进程上打印出“创建完毕”的日志
print(
"torch distributed is already initialized, "
"skipping initialization ...",
flush=True,
)
args.rank = torch.distributed.get_rank() # 取得当前进程的全局序号
args.world_size = torch.distributed.get_world_size() # 取得全局进程的个数
else: # 如果未创建好分布式环境
if args.rank == 0:
print("> initializing torch distributed ...", flush=True)
# 1. 初始化进程,分配GPU,并设置进程大组(group)
if device_count > 0:
device = args.rank % device_count # 1块进程1个GPU。device为GPU编号。例如图例中的进程9,其所在机器上有8块卡。因此进程9使用的gpu编号为8%9=1
if args.local_rank is not None:
assert (
args.local_rank == device
), "expected local-rank to be the same as rank % device-count."
else:
args.local_rank = device
if args.force_device is not None:
print(
f" > forcefully set the device to {args.force_device}, originally {device}"
)
device = args.force_device
torch.cuda.set_device(device) # 为当前进程分配GPU
# 设置进程大组
init_method = "tcp://"
master_ip = os.getenv("MASTER_ADDR", "localhost") # 获取rank=0进程的ip
master_port = os.getenv("MASTER_PORT", "6000") # 获取rank=0进程的端口
init_method += master_ip + ":" + master_port
print(
f" > (rank={args.rank}) initializing process group: "
f"world_size={args.world_size} "
f"backend={args.distributed_backend} "
f"init_method={init_method}",
flush=True,
)
timeout = datetime.timedelta(minutes=args.dist_timeout)
torch.distributed.init_process_group(
backend=args.distributed_backend,
world_size=args.world_size,
rank=args.rank,
init_method=init_method,
timeout=timeout
)
print(f" > (rank={args.rank}) process group initialized")
# 2、制定DP/TP/PP分组策略,设置进程子组(subgroup)
if device_count > 0:
if mpu.model_parallel_is_initialized():
print("model parallel is already initialized")
else:
mpu.initialize_model_parallel( # megatron/mpu/initialize.py
args.tensor_model_parallel_size,
args.pipeline_model_parallel_size,
args.virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size,
)
# 设置DeepSpeed ZeRO-R,对activation进行优化
if args.deepspeed and args.deepspeed_activation_checkpointing:
setup_deepspeed_random_and_activation_checkpointing(args)
总的来说上述代码实现了3个目的:
1.设置分布式环境,初始化进程,分配GPU,设置进程大组(一整个混合并行策略组)
2.指定DP,TP,PP分组策略,设置进程子组
3.设置DeepSpeed ZeRo-R,对activation进行优化。
torch.distributed.init_process_group函数实现了设置进程大组的功能,主要由以下几个概念组成:
backend::即后端。本质上是定义IPC通信机制,对数据实现reduce,gather,broadcast等通信操作。取值有gloo,nccl等。简单来讲可以在使用CPU时选择gloo,使用GPU时,使用nccl。
world_size: 即整个训练项目的所有GPU数量,比如有2台机器,每台4张卡,则最终world_size就是8.
rank: 即每个卡的全局编号,比如2台机器,每台4张卡,则rank编号会从0编号到7,即机器之间也是连续编号。
**init_method:**这个参数指明一个地址,进程组间的进程通过该低质存放的信息进行交流,主要包括:哪些进程应该通信,以及各进程计算进度。比如DP组的两张卡需要做allreduce,则一张卡计算完,可以去这个地址找自己应该与谁通信,并查看当前与自己通信的卡是否计算完毕。为了避免冗余,信息一般只存一份,即存在rank0的进程上。
**time_out:**每个进程间计算速度不一致,因此需要设置一个最大等待时间,不能无限等待。
与之对应的还有一些概念:
**local_rank:**即在本机上的编号,比如2台机器,每台4张卡,每天机器分别有0~3的local_rank编号。
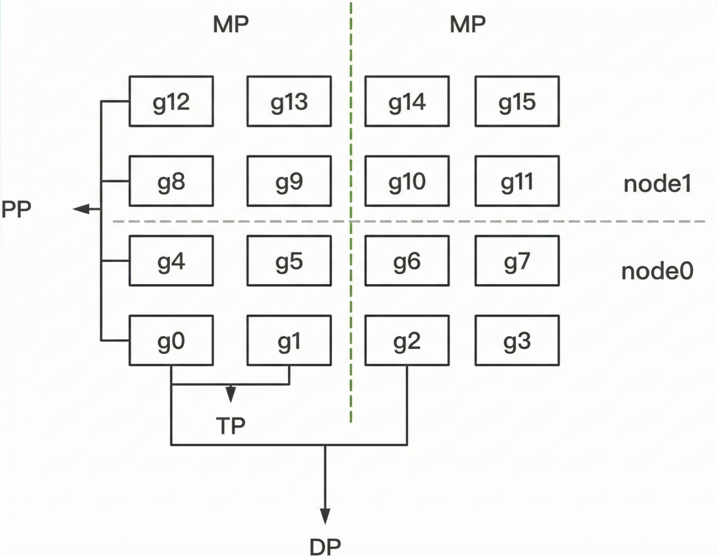
如图为PP,DP,TP并行,其中MP其实是由TP+PP共同决定,一组MP其实就表示一组完整的模型参数,我们知道了MP的数量就可以确定DP的数量,这也是为什么设定一个MP的概念。
TP、DP和PP的设定原则,因为三者的通信量一般而言TP>DP>PP,TP backward的时候需要allreduce得到全局梯度,才能继续下一层的计算,而DP每一层backward是没有依赖的,而PP只有在每一个chunk计算完后,才需要通信将结果给到下一个pp_stage,所以尽量将TP,DP不跨机,而PP跨机。
**DeepSpeed ZeRO-R:**这个主要是针对TP的优化,而不是DP,因为经过TP处理后的输出,会使用allreduce得到全局输出,此时TP rank上都会有同一份activation,这时候的DeepSpeed的处理是将其分片保存,需要时,再allgather回来。
9.MPU(Model Parallel Unit)
mpu.initialize_model_parallel(
args.tensor_model_parallel_size,
args.pipeline_model_parallel_size,
args.virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size,
args.pipeline_model_parallel_split_rank,
...
)
MPU的核心是Megatron-LM分布式训练的调度员,负责组织和管理不同并行方式的GPU进程组,mpu.initialize_model_parallel()就是在创建并行训练的基本结构。
因为在torch.distributed里,默认情况下,GPU进程都是平等的,但在Megatron-LM里,GPU进程角色不同,可以有数据并行组,张量并行组,流水线并行组,Megatron-LM需要手动创建这些并行组,并且分别给予不同的工作,mpu就是用来管理这些并行组的初始化、查询和使用的。
那么initialize_model_parallel具体做了什么呢?
def initialize_model_parallel(
tensor_model_parallel_size_=1,
pipeline_model_parallel_size_=1,
virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size_=None,
):
"""
Initialize model data parallel groups.
Arguments:
tensor_model_parallel_size: number of GPUs used to parallelize model tensor.
pipeline_model_parallel_size: number of GPUs used to parallelize model pipeline.
Let's say we have a total of 16 GPUs denoted by g0 ... g15 and we
use 2 GPUs to parallelize the model tensor, and 4 GPUs to parallelize
the model pipeline. The present function will
create 8 tensor model-parallel groups, 4 pipeline model-parallel groups
and 8 data-parallel groups as:
8 data_parallel groups:
[g0, g2], [g1, g3], [g4, g6], [g5, g7], [g8, g10], [g9, g11], [g12, g14], [g13, g15]
8 tensor model-parallel groups:
[g0, g1], [g2, g3], [g4, g5], [g6, g7], [g8, g9], [g10, g11], [g12, g13], [g14, g15]
4 pipeline model-parallel groups:
[g0, g4, g8, g12], [g1, g5, g9, g13], [g2, g6, g10, g14], [g3, g7, g11, g15]
2 model-parallel group:
[g0, g1, g4, g5, g8, g9, g12, g13], [g2, g3, g6, g7, g10, g8, g14, g15]
Note that for efficiency, the caller should make sure adjacent ranks
are on the same DGX box. For example if we are using 2 DGX-1 boxes
with a total of 16 GPUs, rank 0 to 7 belong to the first box and
ranks 8 to 15 belong to the second box.
"""
if torch.distributed.get_rank() == 0:
print(
"> initializing tensor model parallel with size {}".format(
tensor_model_parallel_size_
)
)
print( # 打印出流水线模型并行的度
"> initializing pipeline model parallel with size {}".format(
pipeline_model_parallel_size_
)
)
# Get world size and rank. Ensure some consistencies.
assert torch.distributed.is_initialized() # 确保torch已经做了分布式初始化
world_size = torch.distributed.get_world_size() # 得到全局进程的总数
tensor_model_parallel_size = min(tensor_model_parallel_size_, world_size)
pipeline_model_parallel_size = min(pipeline_model_parallel_size_, world_size)
ensure_divisibility( # 后者表示一个完整模型所占的gpu数,我们要保证前者能被后者整除
world_size, tensor_model_parallel_size * pipeline_model_parallel_size
)
# 在codegeex中,TP_size=8, PP_size=1,world_size = 1536,因此DP_size是1536/(8*1) = 192
data_parallel_size = world_size // ( # 根据TP_size和PP_size,求出DP_size
tensor_model_parallel_size * pipeline_model_parallel_size
)
num_tensor_model_parallel_groups = world_size // tensor_model_parallel_size # TP的组数
num_pipeline_model_parallel_groups = world_size // pipeline_model_parallel_size # PP的组数
num_data_parallel_groups = world_size // data_parallel_size # DP的组数
if virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size_ is not None:
global _VIRTUAL_PIPELINE_MODEL_PARALLEL_RANK
global _VIRTUAL_PIPELINE_MODEL_PARALLEL_WORLD_SIZE
_VIRTUAL_PIPELINE_MODEL_PARALLEL_RANK = 0
_VIRTUAL_PIPELINE_MODEL_PARALLEL_WORLD_SIZE = (
virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size_
)
rank = torch.distributed.get_rank() # 获取当前进程的全局rank
# Build the data-parallel groups.(设置DP组)
global _DATA_PARALLEL_GROUP # 保存DP组,如[[0,2], [1,3]...],数字表示进进程的全局序号
assert _DATA_PARALLEL_GROUP is None, "data parallel group is already initialized"
all_data_parallel_group_ranks = []
for i in range(pipeline_model_parallel_size):
start_rank = i * num_pipeline_model_parallel_groups
end_rank = (i + 1) * num_pipeline_model_parallel_groups
for j in range(tensor_model_parallel_size):
ranks = range(start_rank + j, end_rank, tensor_model_parallel_size)
all_data_parallel_group_ranks.append(list(ranks))
group = torch.distributed.new_group(ranks) # 设置DP组
if rank in ranks:
_DATA_PARALLEL_GROUP = group
# Build the model-parallel groups.(设置MP组)
global _MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP # 保存MP组
assert _MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP is None, "model parallel group is already initialized"
for i in range(data_parallel_size):
ranks = [
data_parallel_group_ranks[i]
for data_parallel_group_ranks in all_data_parallel_group_ranks
]
group = torch.distributed.new_group(ranks) # 设置MP组
if rank in ranks:
_MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP = group
# Build the tensor model-parallel groups.(设置TP组)
global _TENSOR_MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP # 保存TP组
assert (
_TENSOR_MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP is None
), "tensor model parallel group is already initialized"
for i in range(num_tensor_model_parallel_groups):
ranks = range(
i * tensor_model_parallel_size, (i + 1) * tensor_model_parallel_size
)
group = torch.distributed.new_group(ranks) # 设置TP组
if rank in ranks:
_TENSOR_MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP = group
# Build the pipeline model-parallel groups and embedding groups
# (first and last rank in each pipeline model-parallel group).(设置PP组与embedding组)
global _PIPELINE_MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP # 设置PP组
global _PIPELINE_GLOBAL_RANKS
assert (
_PIPELINE_MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP is None
), "pipeline model parallel group is already initialized"
global _EMBEDDING_GROUP
assert _EMBEDDING_GROUP is None, "embedding group is already initialized"
for i in range(num_pipeline_model_parallel_groups):
ranks = range(i, world_size, num_pipeline_model_parallel_groups)
group = torch.distributed.new_group(ranks) # 设置PP组
if rank in ranks:
_PIPELINE_MODEL_PARALLEL_GROUP = group
_PIPELINE_GLOBAL_RANKS = ranks
# Setup embedding group (to exchange gradients between
# first and last stages).
if len(ranks) > 1:
embedding_ranks = [ranks[0], ranks[-1]]
else:
embedding_ranks = ranks
group = torch.distributed.new_group(embedding_ranks) # 设置embedding组
if rank in embedding_ranks:
_EMBEDDING_GROUP = group
上面的代码通过torch.distributed.new_group在进程大组下创建子组,即tp,dp,pp的group。
注意除了TP,DP,PP的group,还有一个embedding_group,为什么会有这个?其实因为在计算完梯度,更新embedding权重前,输入和输出层需要进行通信,因为输入和输出共用一份权重,需要将它们的grad进行allreduce。
那么混合并行时,每张GPU的全局索引怎么算的呢?可以抽象为一个高维的坐标系(其实跟二维矩阵求索引是类似的):
其中:
R:全局 rank
T:张量并行索引
D:数据并行索引
P:流水线并行索引
分别是张量、数据、流水线并行的进程数量。
2.模型并行实现细节
1.模型切割设计思想
在megatron中模型切割有两套方案:
1.方案一:先定义出完整的模型,并对模型参数做初始化,然后根据进程id取出相应子模型,搬运到GPU上
2.方案二:直接根据进程id,设计好当前子模型,做参数初始化,搬运到GPU上
这两者的核心差别,在于“随机种子”的设定。
在分布式训练中,随机种子是非常重要的,它关系到模型是否能够复现。例��如我们采取activation checkpoint的技术来节省显存时,在backward过程中我们需要重算forward得到activation,这时候就需要我们完整复现之前forward的过程,各类参数的初始化结果也要和之前完全一致。例如TP时,若两个TP_rank分别初始化一部分参数,则需要使用不同的随机种子,否则两部分参数随机初始化后的结果一样,这不等价于将一整块参数随机初始化再分割。一般在TP/PP组内,设定不同的随机种子。而在DP组内,设定相同的随机种子。
2.定义并搬运模型(get_model)
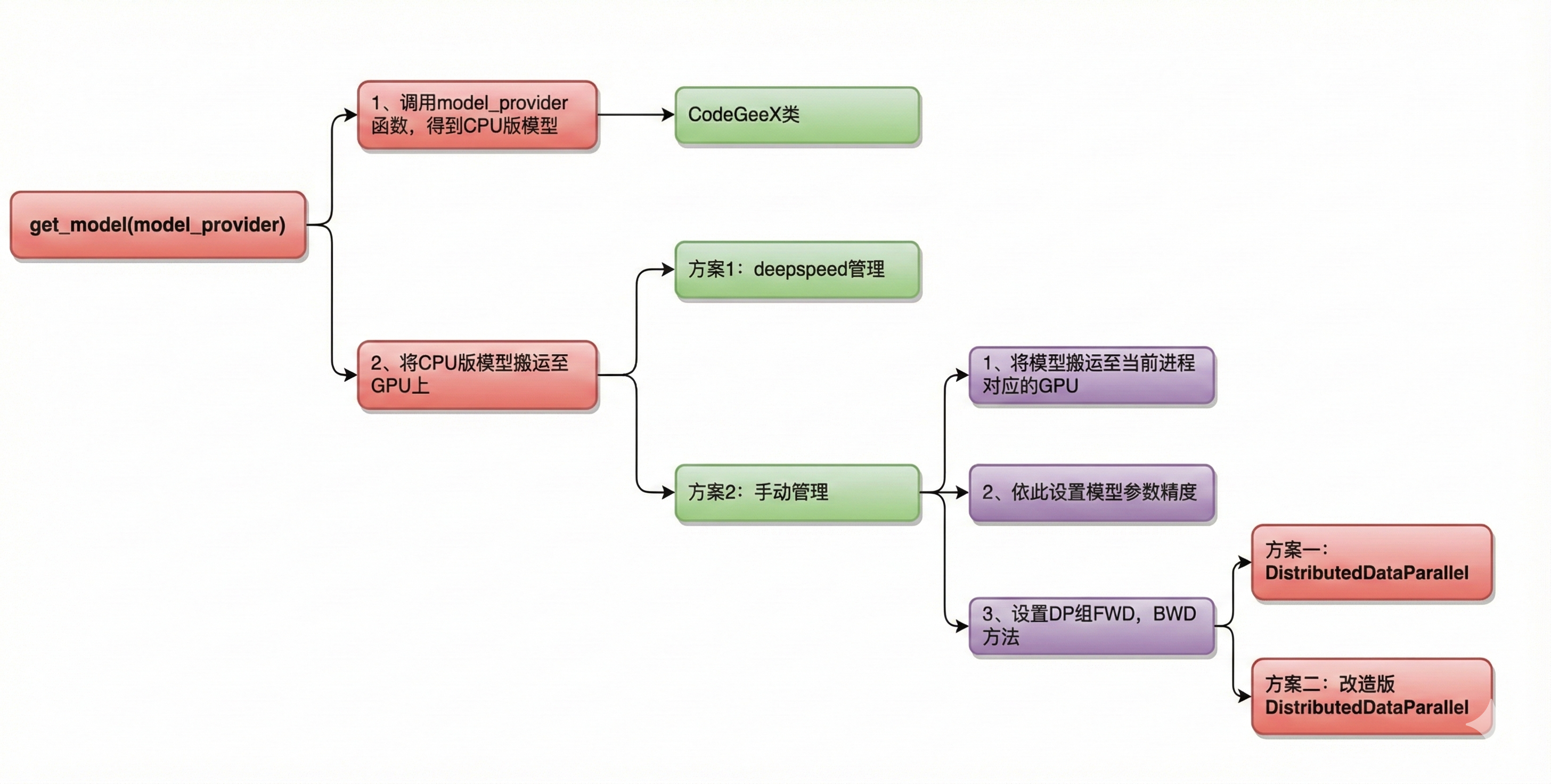
1.在CPU上定义模型。pytorch默认在CPU上定义模型(nn.Module)。model_provider 是一个函数,调用它即可返回CPU版的模型,也就是一个CodeGeeX类。
2.把模型从CPU搬运至GPU上。这里有两种方法可供选择:
方案一:借助deepspeed进行管理。
方案二:手动搬运管理。:
-
- 显式搬运。即手动将模型搬运到当前进程所对应的GPU上
- 权重精度设定。由ZeRO的思想可知,在模型训练中,把权重精度从fp32降至fp16,是一种节省显存的好办法。如果确定使用这种优化办法,将模型搬运到GPU上后,我们需要修改精度。
- 初始化DP组��。这里指的是定义DP组间forward、backward和梯度计算与通讯等方法。在Megatron中,TP和PP组的这些方法是人为定义的(在定义CPU模型时已设置好,我们将在下文讲
CodeGeeX细节时看到),而DP组则是可以用现成的(torch的DistributedDataParallel)。在具体使用时,我们可以:(1)直接调用DistributedDataParallel。或(2)在DistributedDataParallel这个类的基础上做一些改进,例如增加对碎片化内存的管理,对计算梯度时的精度控制等。
get_model的代码:
def get_model(model_provider_func):
"""Build the model."""
args = get_args()
# 1、定义并构建CPU版模型
if ( # 1.1、当分布式进行框架采用virtual pipeline (是NVDIA后续提出的对Megatron的优化方法)
mpu.get_pipeline_model_parallel_world_size() > 1
and args.virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size is not None
):
model = []
for i in range(args.virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_size):
mpu.set_virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_rank(i)
# Set pre_process and post_process only after virtual rank is set.
pre_process = mpu.is_pipeline_first_stage()
post_process = mpu.is_pipeline_last_stage()
this_model = model_provider_func(
pre_process=pre_process, post_process=post_process
)
model.append(this_model)
else: # 1.2 其余情况
# 判断当前进程是否是PP组的第一个进程(例如第一部分图例中PP组的g0)
pre_process = mpu.is_pipeline_first_stage()
# 判断当前进程是否是PP组的最后一个进程(例如第一部分图例中PP组的g12)
post_process = mpu.is_pipeline_last_stage()
# 构建CPU版CodeGeeX模型
model = model_provider_func(pre_process=pre_process, post_process=post_process)
...
# 2、将模型从CPU搬运到GPU上
# 2.1 如果采用Megatron-DeepSpeed的方式,则直接返回模型,后面的搬运,数据并行等工作将由deepspeed来完成
# ref:https://www.deepspeed.ai/tutorials/megatron/
if args.deepspeed:
return model
# 将当前进程所维护的模型,从CPU搬运到GPU上(GPU即为在初始化时为当前进程分配的那块GPU)
print(f" > moving model to GPU ...", flush=True)
for model_module in model:
model_module.cuda(torch.cuda.current_device())
print(f" > moving to GPU done", flush=True)
# fp16转换(pytorch默认模型参数精度为fp32,依需决定计算过程中是否要转成fp16,节省显存)
if args.fp16 or args.bf16:
print(f" > converting model to fp16 ...", flush=True)
model = [Float16Module(model_module, args) for model_module in model]
print(f" > converting to fp16 done", flush=True)
# 采用pytorch定义的DistributedDataParallel管理数据并行
if args.DDP_impl == "torch":
i = torch.cuda.current_device()
model = [
torchDDP(
model_module,
device_ids=[i],
output_device=i,
process_group=mpu.get_data_parallel_group(), # 数据并行的组
)
for model_module in model
]
return model
# 采用自定义的DistributedDataParallel管理数据并行
# 即在pytorch的DistributedDataParallel的基础上,自己再定义内存管理、梯度精度等计算方式,更有效利用显存
if args.DDP_impl == "local": # 自定义的数据并行类在megatron/model/distributed.py下
print(f" > creating DDP model ...", flush=True)
model = [
LocalDDP(
model_module,
args.accumulate_allreduce_grads_in_fp32,
args.use_contiguous_buffers_in_ddp,
)
for model_module in model
]
print(f" > creating DDP model done", flush=True)
return model
raise NotImplementedError(
"Unknown DDP implementation specified: {}. " "Exiting.".format(args.DDP_impl)
)
因为模型的首尾两层,存在embedding和embedding逆的操作,和中间层会有一些区别,因此使用pre_process, post_process进行区分。
3.TP下的分布�式模型单元
主要包括**Embedding、ParallelSelfAttention、ParallelMLP、_VocabParallelCrossEntropy**都是继承于MegatronModule,而不是nn.Module,因此首先介绍一下nn.Module。
MegatronModule
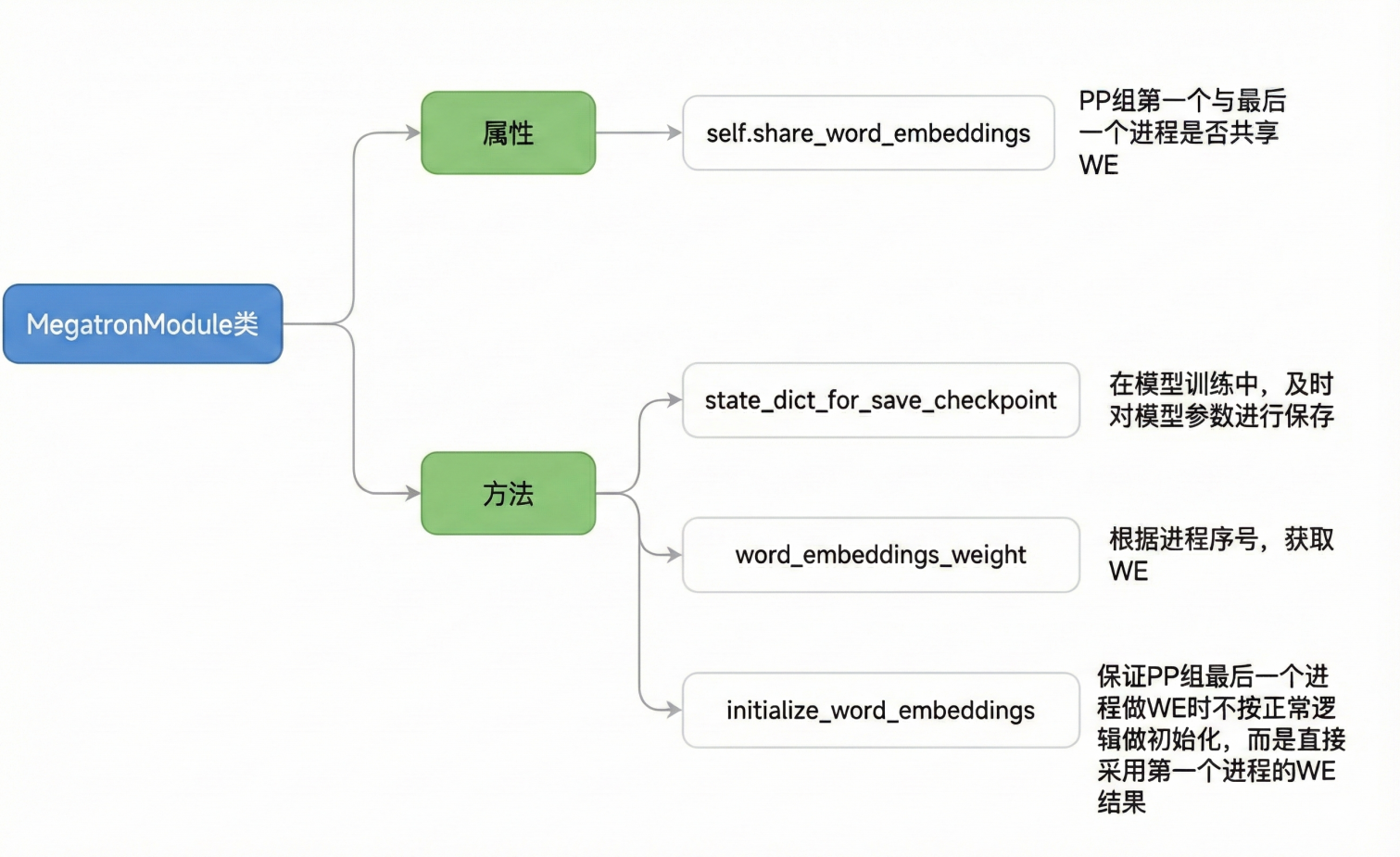
class MegatronModule(torch.nn.Module):
"""Megatron specific extensions of torch Module with support
for pipelining."""
def __init__(self, share_word_embeddings=True):
super(MegatronModule, self).__init__()
# input和output是否要共享一套WE
self.share_word_embeddings = share_word_embeddings
def state_dict_for_save_checkpoint(
self, destination=None, prefix="", keep_vars=False
):
"""Use this function to override the state dict for
saving checkpoints."""
# 模型训练中,及时将参数保存到指定位置(设置checkpoint),
# 这样在训练出问题时,可以从checkpoint点重新load参数,继续训练
return self.state_dict(destination, prefix, keep_vars)
def word_embeddings_weight(self):
"""获取word_embedding"""
if mpu.is_pipeline_first_stage(ignore_virtual=True):
return self.language_model.embedding.word_embeddings.weight
if mpu.is_pipeline_last_stage(ignore_virtual=True):
if not self.share_word_embeddings:
raise Exception( # 强制要求共享一套embedding
"word_embeddings_weight() called for last "
"stage, but share_word_embeddings is false"
)
return self.word_embeddings.weight # 参见initialize_word_embeddings中WE的定义
raise Exception( # 如果当前进程是PP组的中间进程,则其上未维护WE,因此当然获取不到
"word_embeddings_weight() should be " "called for first and last stage only"
)
def initialize_word_embeddings(self, init_method_normal):
"""强制PP组最后一个进程初始化WE时,直接使用PP组第一个进程的WE"""
args = get_args()
if not self.share_word_embeddings: # 强制share embeddingg
raise Exception(
"initialize_word_embeddings() was called but "
"share_word_embeddings is false"
)
# PP组并行度为1时,第一层和最后一层都在一块GPU上,天然共享WE,无需做强制
if args.pipeline_model_parallel_size == 1:
return
# ---------------------------------------------------
# 如果流水线并行的度不为1时,依次做三件事:
# 【初始化时】:
# 1、在PP组最后一个进程上初始化一个WE,令其取值全为0
# 2、在PP组第一个进程与最后一个进程间做一次AllReduce,保证两者的WE完全一致
# 【训练时】:
# 3、每次想在PP组第一个/最后一个进程上使用WE时,要做一次通信,保证两者用的WE完全一致
if mpu.is_pipeline_last_stage(): # 若当前进程是PP组最后一个进程
assert not mpu.is_pipeline_first_stage()
self._word_embeddings_for_head_key = "word_embeddings_for_head"
# 初始化一个WE(已按vocab_size维度切割,可参见Megatron原理篇对WE的讲解)
# VocabParallelEmbedding将在下文详细讲解
self.word_embeddings = mpu.VocabParallelEmbedding(
args.padded_vocab_size, # vocab_size
args.hidden_size, # embed_dim
init_method=init_method_normal(args.init_method_std), # 初始化方法(在model/utils.py下)
)
# 用0填充WE(等待下面做AllReduce后取得第一个进程上的WE)
self.word_embeddings.weight.data.fill_(0)
self.word_embeddings.weight.shared = True
if torch.distributed.is_initialized():
if mpu.is_pipeline_first_stage() or mpu.is_pipeline_last_stage(): # 若当前进程是PP组第一个或最后一个进程
# 在两进程间做AllReduce,保证它们使用的WE完全一致
# mpu.get_embedding_group:在源码解读1中讲过,是除DP/TP/PP之外设置的又一进程组,
# 主要就是用来做关于WE的通讯
torch.distributed.all_reduce(
self.word_embeddings_weight().data, group=mpu.get_embedding_group()
)
else:
print(
"WARNING! Distributed processes aren't initialized, so "
"word embeddings in the last layer are not initialized. "
"If you are just manipulating a model this is fine, but "
"this needs to be handled manually. If you are training "
"something is definitely wrong."
)
这里主要做了一些处理,一个是对于输入层的embedding和输出层的lm_head做一个权重共享。另外一方面,对于PP的场景来说,输入和输出分布在不同的GPU上,因此每次使用WE时都要做一次allreduce进行数据同步。
Embedding
class Embedding(MegatronModule):
"""Language model embeddings.
Arguments:
hidden_size: hidden size
vocab_size: vocabulary size
max_sequence_length: maximum size of sequence. This
is used for positional embedding
embedding_dropout_prob: dropout probability for embeddings
init_method: weight initialization method
num_tokentypes: size of the token-type embeddings. 0 value
will ignore this embedding
"""
def __init__(
self,
hidden_size, # 每个token的向量维度
vocab_size, # 词表大小
max_sequence_length, # 最长序列长度
embedding_dropout_prob, # dropout probability for embeddings
init_method, # 初始化权重的方法
num_tokentypes=0, # 类似于Bert中的segment type
):
super(Embedding, self).__init__()
args = get_args()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.init_method = init_method
self.num_tokentypes = num_tokentypes
self.max_sequence_length = max_sequence_length
# WE size: (vocab_size//TP_N, hidden_size)
# TP_N表示TP组模型并行度
self.word_embeddings = mpu.VocabParallelEmbedding(
vocab_size, self.hidden_size, init_method=self.init_method)
self._word_embeddings_key = 'word_embeddings'
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
# PE size: (max_seq_len, hidden_size)
self.position_embeddings = torch.nn.Embedding(
max_sequence_length, self.hidden_size)
self.position_embeddings = self.position_embeddings.half()
self._position_embeddings_key = 'position_embeddings'
# Initialize the position embeddings.
self.init_method(self.position_embeddings.weight)
# TE_size:(num_tokentypes, hidden_size)
# TE类似于Bert中的segment embedding
self._tokentype_embeddings_key = 'tokentype_embeddings'
if self.num_tokentypes > 0:
self.tokentype_embeddings = torch.nn.Embedding(self.num_tokentypes,
self.hidden_size)
# Initialize the token-type embeddings.
self.init_method(self.tokentype_embeddings.weight)
else:
self.tokentype_embeddings = None
# Embeddings dropout
self.embedding_dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(embedding_dropout_prob)
def add_tokentype_embeddings(self, num_tokentypes):
"""如果在pretrain阶段未定义TE,而在fine-tune阶段TE,则可通过此函数添加
"""
if self.tokentype_embeddings is not None:
raise Exception('tokentype embeddings is already initialized')
if torch.distributed.get_rank() == 0:
print('adding embedding for {} tokentypes'.format(num_tokentypes),
flush=True)
self.num_tokentypes = num_tokentypes
self.tokentype_embeddings = torch.nn.Embedding(num_tokentypes,
self.hidden_size)
# Initialize the token-type embeddings.
self.init_method(self.tokentype_embeddings.weight)
def forward(self, input_ids, position_ids, tokentype_ids=None):
"""定义输入X过embedding层的计算方法
"""
# words_embeddings size = (b, seq_len, hidden_size)
# 再次注意:self.word_embeddings做forward时,最终的输出结果时AllReduce
words_embeddings = self.word_embeddings(input_ids)
# position_embeddings size = (b, seq_len, hidden_size)
position_embeddings = self.position_embeddings(position_ids)
# embedding = WE + PE
# embedding size = (b, seq_len, hidden_size)
embeddings = words_embeddings + position_embeddings
# 依需要决定是否增加TE
if tokentype_ids is not None:
assert self.tokentype_embeddings is not None
embeddings = embeddings + self.tokentype_embeddings(tokentype_ids)
else:
assert self.tokentype_embeddings is None
# Dropout.
embeddings = self.embedding_dropout(embeddings)
return embeddings
def state_dict_for_save_checkpoint(
self, destination=None, prefix='', keep_vars=False,
):
"""For easy load.
在模型训练过程中及时读取当前参数,方便及时保存(做checkpoint)
篇幅限制,这里不展示细节
"""
...
def load_state_dict(self, state_dict, strict=True):
"""Customized load.
用于模型的重载。例如训到一半挂掉了,我们就重新初始化一个新模型,
重载上个checkpoint保存下的权重。
篇幅限制,这里不展示细节
"""
...
这里的TE其实就是Bert里面的segment embedding概念,主要是用来区分当前token在句子的第几句(假设有两句话,4个词,则可能是[0,0,1,1])。需要注意一点,这里的position embedding和tokentype embedding 都只和输入有关,所以��大小和输入数据一致,而不像WE需要做切分。self.word_embeddings = mpu.VocabParallelEmbedding(vocab_size, self.hidden_size, init_method=self.init_method) 注意这里调用的是VocabParallelEmbedding,所以会根据vocab_size, self.hidden_size以及tp并行数通过VocabParallelEmbedding对embedding层做切分,所以这里self.word_emeddings是已经切好的。
VocabParallelEmbedding
class VocabParallelEmbedding(torch.nn.Module):
"""Embedding parallelized in the vocabulary dimension.
This is mainly adapted from torch.nn.Embedding and all the default
values are kept.
Arguments:
num_embeddings: vocabulary size.
embedding_dim: size of hidden state.
init_method: method to initialize weights.
"""
def __init__(self, num_embeddings, embedding_dim, init_method=init.xavier_normal_):
super(VocabParallelEmbedding, self).__init__()
# Keep the input dimensions.
self.num_embeddings = num_embeddings # vocab_size
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim # hidden_state.
# Set the detauls for compatibility.
self.padding_idx = None
self.max_norm = None
self.norm_type = 2.0
self.scale_grad_by_freq = False
self.sparse = False
self._weight = None
# 当前进程所在TP组进程总数
self.tensor_model_parallel_size = get_tensor_model_parallel_world_size()
# 根据当前进程在TP组中的序号,确定其所需维护的WE部分,沿着vocab维度对WE进行切割
# 例如,进程id=0, 维护词表序号[0,5)范围内的数据;进程id=1,维护[5,10)
(
self.vocab_start_index,
self.vocab_end_index,
) = VocabUtility.vocab_range_from_global_vocab_size(
self.num_embeddings,
get_tensor_model_parallel_rank(),
self.tensor_model_parallel_size,
)
# 计算当前进程维护的词表大小
self.num_embeddings_per_partition = (
self.vocab_end_index - self.vocab_start_index
)
# 对WE做初始化
args = get_args() # 读取预训练参数配置
if args.use_cpu_initialization: # CPU上做初始化
self.weight = Parameter(#生成一个切分后大小的weight权重
torch.empty(
self.num_embeddings_per_partition,
self.embedding_dim,
dtype=args.params_dtype,
# dtype=torch.float32,
)
)
# 在CPU上初始化一个完整的WE,并且进行切片填充当前的self.weight(随机种子在初始化分布式中已设定好,不用变)
_initialize_affine_weight_cpu(
self.weight,
self.num_embeddings,
self.embedding_dim,
self.num_embeddings_per_partition,
0,
init_method, # 初始化权重的方法,例如xavier之类
)
else: # 在GPU上做初始化
self.weight = Parameter( # 生成一个切割好的WE
torch.empty(
self.num_embeddings_per_partition,
self.embedding_dim,
device=torch.cuda.current_device(),
dtype=args.params_dtype,
# dtype=torch.float32,
)
)
# 在GPU上做初�始化,注意TP组内不同进程采用不同的随机种子
_initialize_affine_weight_gpu(
self.weight, init_method, partition_dim=0, stride=1
)
def forward(self, input_):
"""定义输入X过WE的计算方法,输出结果已经过AllReduce"""
if self.tensor_model_parallel_size > 1: # 如果使用TP
# 如果在当前进程维护的WE上,找不到对应的单词,那么对应位置就赋0
# 例如当前的数据的tokenid是:[2,7,1,5],当前维护的词表是[0,1,2](start_index=0, end_index = 3),
# 则mask之后的数据为[2,0,1,0]
# Build the mask.
input_mask = (input_ < self.vocab_start_index) | (
input_ >= self.vocab_end_index
)
# Mask the input.
masked_input = input_.clone() - self.vocab_start_index
masked_input[input_mask] = 0
else:
masked_input = input_
# 输入X,过当前进程维护的部分WE的结果
output_parallel = F.embedding(
masked_input, # tensor containing indices into the embedding matrix
self.weight, # 切割好的word embedding的权重
self.padding_idx,
self.max_norm,
self.norm_type,
self.scale_grad_by_freq,
self.sparse,
)
# 当前词表不维护的部分,都设为0
if self.tensor_model_parallel_size > 1:
output_parallel[input_mask, :] = 0.0 #
# 将TP组各GPU上的结果做AllReduce
output = reduce_from_tensor_model_parallel_region(output_parallel)
return output
def _initialize_affine_weight_cpu(...):
"""CPU版权重初始化。这个不难,大��家可以自己阅读"""
...
def _initialize_affine_weight_gpu(...):
"""GPU版权重初始化。特别关注设置随机种子部分"""
...
# 借助deepspeed或自定义的get_cuda_rng_tracker方法,对随机种子进行操作
# get_cuda_rng_tracker细节,大家可自行阅读源码
if ds_checkpointing.is_configured():
global get_cuda_rng_tracker
get_cuda_rng_tracker = ds_checkpointing.get_cuda_rng_tracker
with get_cuda_rng_tracker().fork():
init_method(weight)
在这里主要讲解两个细节:
1.注意到初始化的时候,有两种初始化方法:
(1) 在CPU上初始化,即先生成一个完整的weight,然后分别切片分发到每个GPU上
(2) 直接在各个GPU上初始化每个分片
第一种方法可以和单卡视角完全对齐,但是第二种不行,因为每个GPU上随机种子不一样,分别初始化,而单卡视角是一个矩阵用一个随机种子初始化。而方法1通常是用来和单卡视角做精度对齐,方法二则是实际工程使用的,因为在实际工业使用中,CPU上初始化大矩阵很容易就OOM,因此才需要分别在每个GPU上分片初始化。
2.注意到forward过程的逻辑:
首先通过范围判断,得到一个跟输入大小一样的input_mask,来处理不在当前rank范围内的token,将他们都设置成true,其它在本rank的则都是false,紧接着复制输入input,减去self.vocab_start_index,则在当前rank上的那些token_id都被映射到了当前的local_vocab范围内,因为每个rank上的vocab都是[0,n],所以需要映射,紧接着,再根据刚才的input_mask把那些不在当前rank处理范围内的token的id都映射到0(不映射超出当前rank的vocab范围会报错)。
然后使用F.embedding操作,其实就是一个查表操作,通过给定的self.weight(要查的表),和需要查找的索引集合masked_input去找到对应的token的embedding,而因为前面将不在当前rank处��理范围内的token的id都映射成了0,则这些位置的embedding都被赋值成了0对应的embedding,因此需要移除掉这些垃圾数据,即设为0.0(为了后续reduce的正确性),最后做一个allreduce,即可让每个tp_rank都得到输入input的全局embedding。
ColumnParallelLinear
class ColumnParallelLinear(torch.nn.Module):
"""Linear layer with column parallelism.
The linear layer is defined as Y = XA + b. A is parallelized along
its second dimension as A = [A_1, ..., A_p].
Arguments:
input_size: first dimension of matrix A.
output_size: second dimension of matrix A.
bias: If true, add bias
gather_output: If true, call all-gether on output and make Y avaiable
to all GPUs, otherwise, every GPU will have its output
which is Y_i = XA_i
init_method: method to initialize weights. Note that bias is always set
to zero.
stride: For the strided linear layers.
keep_master_weight_for_test: This was added for testing and should be
set to False. It returns the master weights
used for initialization.
skip_bias_add: This was added to enable performance optimations where bias
can be fused with other elementwise operations. we skip
adding bias but instead return it.
"""
# 该类定义了切割后的权重W,例如对上图来说,W1和W2都可分别视为该类的一个实例
def __init__(
self,
input_size, # W的第一个维度
output_size, # W的第二个维度
bias=True, # 是否需要引入bias
gather_output=True, # 决定是否要将Y1和Y2做all-gather
init_method=init.xavier_normal_,
stride=1,
keep_master_weight_for_test=False,
skip_bias_add=False,
params_dtype=None,
skip_init=False,
device=None,
):
super(ColumnParallelLinear, self).__init__()
# Keep input parameters
self.input_size = input_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.gather_output = gather_output
# Divide the weight matrix along the last dimension.
# 当前进程所在TP组的总进程数
world_size = get_tensor_model_parallel_world_size()
# 每块GPU上维护的hidden_size的大小,等于 原hidden_zize // TP组总进程数
self.output_size_per_partition = divide(output_size, world_size)
self.skip_bias_add = skip_bias_add
self.params_dtype = params_dtype
self.device = device
# Parameters.
# Note: torch.nn.functional.linear performs XA^T + b and as a result
# Initialize weight.
args = get_args() # 取得命令行所有的参数
if not skip_init:
if args.use_cpu_initialization: # CPU上初始化
self.weight = Parameter(
torch.empty(
self.output_size_per_partition,
self.input_size,
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype,
)
)
self.master_weight = _initialize_affine_weight_cpu( #
self.weight,
self.output_size,
self.input_size,
self.output_size_per_partition,
0,
init_method,
stride=stride,
return_master_weight=keep_master_weight_for_test,
)
else: # GPU上初始化
self.weight = Parameter(
torch.empty(
self.output_size_per_partition,
self.input_size,
device=self.device if self.device is not None else torch.cuda.current_device(),
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype,
)
)
_initialize_affine_weight_gpu(
self.weight, init_method, partition_dim=0, stride=stride
)
else:
self.register_parameter("weight", None)
# 对bias做处理,道理同weight
if bias and not skip_init:
if args.use_cpu_initialization: # CPU上初始化
self.bias = Parameter(
torch.empty(self.output_size_per_partition,
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype)
)
else:
self.bias = Parameter( # GPU上初始化
torch.empty(
self.output_size_per_partition,
device=self.device if self.device is not None else torch.cuda.current_device(),
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype,
)
)
set_tensor_model_parallel_attributes(self.bias, True, 0, stride)
# Always initialize bias to zero.
with torch.no_grad():
self.bias.zero_()
else:
self.register_parameter("bias", None)
def forward(self, input_):
# 定义列切割中的f算子
# 调用copy_to_tensor_model_parallel_region则新建一个_CopyToModelParallelRegion实例(见下)
input_parallel = copy_to_tensor_model_parallel_region(input_)
bias = self.bias if not self.skip_bias_add else None # 定义bias
output_parallel = F.linear(input_parallel, self.weight, bias) # X * 切割好的权重
# 决定是否要对每个进程上的输出结果做all=gather
if self.gather_output:
# 定义列切割中的g算子
# 调用gather_from_tensor_model_parallel_region则新建一个_GatherFromModelParallelRegion实例(见下)
output = gather_from_tensor_model_parallel_region(output_parallel) # 把各GPU上的输出按照列gather起来后,作为最终输出
else:
output = output_parallel # 否则最终输出还是自己算的那块GPU
output_bias = self.bias if self.skip_bias_add else None
return output, output_bias
# �列切割中的f与g
class _CopyToModelParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""Pass the input to the model parallel region."""
# 列切割下的f算子
# forward:copy输入
# backward:对梯度做AllReduce
@staticmethod
def symbolic(graph, input_):
return input_
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
return input_
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
return _reduce(grad_output)
class _GatherFromModelParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""Gather the input from model parallel region and concatinate."""
# 列切割中的g算子
# forward:All-Gather输出
# backward:对梯度,沿着列方向做split
@staticmethod
def symbolic(graph, input_):
return _gather(input_)
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
return _gather(input_)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
return _split(grad_output)
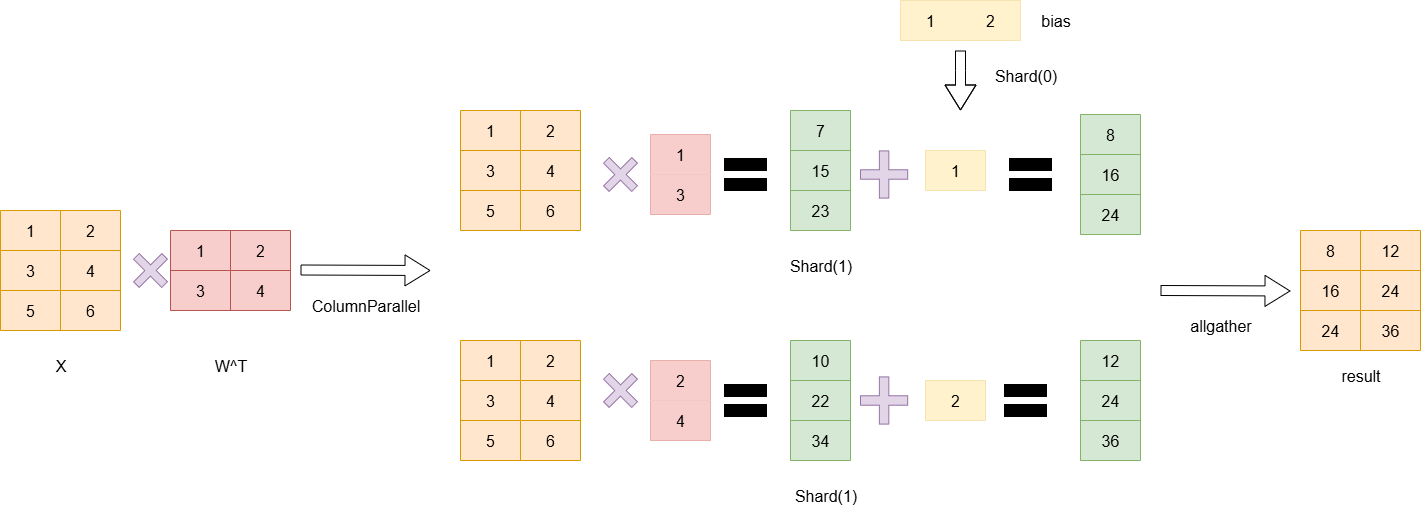
这里主要注意_CopyToModelParallelRegion和_GatherFromModelParallelRegion两个类:
首先前者是在列切下的f算子,在做forward的时候,因为每个tp_rank上都需要完整的输入,因此直接返回完整输入即可;而在backward的时候,此时,,此时每张卡上得到的对X的导数都是partial状态,因此需要做一个allreduce。
而后者是在最后tp_rank分别得到输出结果后,此时每个rank的数据相对整个数据是被切分成了tp_nums份的,此时如果后面没有RowParallel层了,则需要做一个allgather的操作,得到完整输出,而在backward过程,每个rank的输出是通过allgather得到完整形状的,因此反向时,需要再按tp维度进行split得到每个rank需要的那部分梯度。
RowParallel
class RowParallelLinear(torch.nn.Module):
"""Linear layer with row parallelism.
The linear layer is defined as Y = XA + b. A is parallelized along
its first dimension and X along its second dimension as:
- -
| A_1 |
| . |
A = | . | X = [X_1, ..., X_p]
| . |
| A_p |
- -
Arguments:
input_size: first dimension of matrix A.
output_size: second dimension of matrix A.
bias: If true, add bias. Note that bias is not parallelized.
input_is_parallel: If true, we assume that the input is already
split across the GPUs and we do not split
again.
init_method: method to initialize weights. Note that bias is always set
to zero.
stride: For the strided linear layers.
keep_master_weight_for_test: This was added for testing and should be
set to False. It returns the master weights
used for initialization.
skip_bias_add: This was added to enable performance optimations where bias
can be fused with other elementwise operations. we skip
adding bias but instead return it.
"""
def __init__(
self,
input_size,
output_size,
bias=True,
input_is_parallel=False,
init_method=init.xavier_normal_,
stride=1,
keep_master_weight_for_test=False,
skip_bias_add=False,
params_dtype=None,
skip_init=False,
device=None,
):
super(RowParallelLinear, self).__init__()
# Keep input parameters
self.input_size = input_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.input_is_parallel = input_is_parallel
# Divide the weight matrix along the last dimension.
world_size = get_tensor_model_parallel_world_size()
self.input_size_per_partition = divide(input_size, world_size)
self.skip_bias_add = skip_bias_add
self.params_dtype = params_dtype
self.device = device
# Parameters.
# Note: torch.nn.functional.linear performs XA^T + b and as a result
# we allocate the transpose.
# Initialize weight.
args = get_args()
if not skip_init:
if args.use_cpu_initialization:
self.weight = Parameter(
torch.empty(
self.output_size,
self.input_size_per_partition,
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype,
)
)
self.master_weight = _initialize_affine_weight_cpu(
self.weight,
self.output_size,
self.input_size,
self.input_size_per_partition,
1,
init_method,
stride=stride,
return_master_weight=keep_master_weight_for_test,
)
else:
self.weight = Parameter(
torch.empty(
self.output_size,
self.input_size_per_partition,
device=self.device if self.device is not None else torch.cuda.current_device(),
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype,
)
)
_initialize_affine_weight_gpu(
self.weight, init_method, partition_dim=1, stride=stride
)
else:
self.register_parameter("weight", None)
if bias and not skip_init:
if args.use_cpu_initialization:
self.bias = Parameter(
torch.empty(self.output_size,
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype)
)
else:
self.bias = Parameter(
torch.empty(
self.output_size,
device=self.device if self.device is not None else torch.cuda.current_device(),
dtype=self.params_dtype if self.params_dtype is not None else args.params_dtype,
)
)
# Always initialize bias to zero.
with torch.no_grad():
self.bias.zero_()
else:
self.register_parameter("bias", None)
def forward(self, input_):
# Set up backprop all-reduce.
if self.input_is_parallel:
input_parallel = input_
else:
input_parallel = scatter_to_tensor_model_parallel_region(input_)
# Matrix multiply.
output_parallel = F.linear(input_parallel, self.weight)
# All-reduce across all the partitions.
output_ = reduce_from_tensor_model_parallel_region(output_parallel)
if not self.skip_bias_add:
output = output_ + self.bias if self.bias is not None else output_
output_bias = None
else:
output = output_
output_bias = self.bias
return output, output_bias
# 行切割中的f和g算子
class _ScatterToModelParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""Split the input and keep only the corresponding chuck to the rank."""
# 行切割中的f算子
# forward:沿列split输入
# backward:all-gather梯度
@staticmethod
def symbolic(graph, input_):
return _split(input_)
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
return _split(input_)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
return _gather(grad_output)
class _ReduceFromModelParallelRegion(torch.autograd.Function):
"""All-reduce the input from the model parallel region."""
# 行切割中的g算子
# forward:AllReduce输出
# backward:正常计算梯度,GPU间无需做任何通讯
@staticmethod
def symbolic(graph, input_):
return _reduce(input_)
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input_):
return _reduce(input_)
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
return grad_output
这里需要注意f:_ScatterToModelParallelRegion和g:_ReduceFromModelParallelRegion这两个类:
因为weight被行切了,因此对应的输入需要列切(这就是f在forward需要做的),然后每部分分别做乘积,最后每个rank都会得到一份输出,此时是一个partial的状态,因此需要做allreduce得到全局数据(这就是g需要在foward做的)。而backward的时候,因为此时每张卡都在forward过程做了allreduce,都有全局输出Y,所以backward每张卡都用同样的Y计算梯度即可,不需要做通信操作,所以直接返回grad即可(g做)。而由于forward过程,把输入切分成了多份,此时每张卡算出了对输入X的梯度,都是一部分的,需要调用all gather拼起来整个梯度(f做)。
CrossEntropy
class _VocabParallelCrossEntropy(torch.autograd.Function):
"""
分布式计算Loss
"""
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, vocab_parallel_logits, target):
# 1. logit - global max(logit)操作,主要目的是防溢出
logits_max = torch.max(vocab_parallel_logits, dim=-1)[0] # (b, s, 1)
torch.distributed.all_reduce( # (b, s, 1)
logits_max,
op=torch.distributed.ReduceOp.MAX, # 找全局最大值
group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group(),
)
# Subtract the maximum value.
vocab_parallel_logits.sub_(logits_max.unsqueeze(dim=-1)) # 原始GPU上维护的logits减去每行最大值(防止溢出)
# 2、根据当前进程id,取出当前进程所维护词表序号等信息
# 函数,能够获取当前进程所维护词表的start_index和end_index
get_vocab_range = VocabUtility.vocab_range_from_per_partition_vocab_size
# 这块GPU上logits最后一维的大小,等于所维护的词表的大小(v/N)
partition_vocab_size = vocab_parallel_logits.size()[-1]
# 取得当前进程所在TP组中的序号
rank = get_tensor_model_parallel_rank()
# 取得当前进程所在TP组的总进程数
world_size = get_tensor_model_parallel_world_size()
# 取得当前进程所维护的词表的start_index和end_index
vocab_start_index, vocab_end_index = get_vocab_range(
partition_vocab_size, rank, world_size
)
# 3. 基于真值,取出每个token在真值位置上的logit(即和真值的相似度)
# Create a mask of valid vocab ids (1 means it needs to be masked)
target_mask = (target < vocab_start_index) | (target >= vocab_end_index) # target = (b, s)
masked_target = target.clone() - vocab_start_index
masked_target[target_mask] = 0
# Get predicted-logits = logits[target].
# For Simplicity, we convert logits to a 2-D tensor with size
# [*, partition-vocab-size] and target to a 1-D tensor of size [*].
logits_2d = vocab_parallel_logits.view(-1, partition_vocab_size) # (b*s, v/N)
masked_target_1d = masked_target.view(-1) # (b*s)
arange_1d = torch.arange( # [b*s]
start=0, end=logits_2d.size()[0], device=logits_2d.device
)
# logits_2d[arange_1d, masked_target_1d]:
# tensor的切片操作。logits_2d表示当前每个token对当前vocab表中每一个token的相似度,即表示为logit值。arange_1d和masked_target_1d每一对数组成一个行列的index[i,j],表示从第i个token中这一行logits中,取第j个位置的logit。从而取出真值位置的logit。
predicted_logits_1d = logits_2d[arange_1d, masked_target_1d] # (b*s)
predicted_logits_1d = predicted_logits_1d.clone().contiguous()
predicted_logits = predicted_logits_1d.view_as(target) # (b, s)
predicted_logits[target_mask] = 0.0
# All reduce is needed to get the chunks from other GPUs.
torch.distributed.all_reduce( # allreduce之后得到的logit矩阵为(b, s),每一个位置表示对应真值位置的预测logit
predicted_logits,
op=torch.distributed.ReduceOp.SUM,
group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group(),
)
# Sum of exponential of logits along vocab dimension across all GPUs.
exp_logits = vocab_parallel_logits # (b, s, v/N)
torch.exp(vocab_parallel_logits, out=exp_logits)
sum_exp_logits = exp_logits.sum(dim=-1) # (b, s)
torch.distributed.all_reduce(
sum_exp_logits,
op=torch.distributed.ReduceOp.SUM,
group=get_tensor_model_parallel_group(),
)
# 4. 计算Loss = log(sum(exp(logits))) - predicted-logit.
loss = torch.log(sum_exp_logits) - predicted_logits # (b, s)
# Store softmax, target-mask and masked-target for backward pass.
exp_logits.div_(sum_exp_logits.unsqueeze(dim=-1))
ctx.save_for_backward(exp_logits, target_mask, masked_target_1d)
return loss
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
# Retreive tensors from the forward path.
softmax, target_mask, masked_target_1d = ctx.saved_tensors
# All the inputs have softmax as their gradient.
grad_input = softmax
# For simplicity, work with the 2D gradient.
partition_vocab_size = softmax.size()[-1]
grad_2d = grad_input.view(-1, partition_vocab_size)
# Add the gradient from matching classes.
arange_1d = torch.arange(start=0, end=grad_2d.size()[0], device=grad_2d.device)
grad_2d[arange_1d, masked_target_1d] -= 1.0 - target_mask.view(-1).float()
# Finally elementwise multiplication with the output gradients.
grad_input.mul_(grad_output.unsqueeze(dim=-1))
return grad_input, None
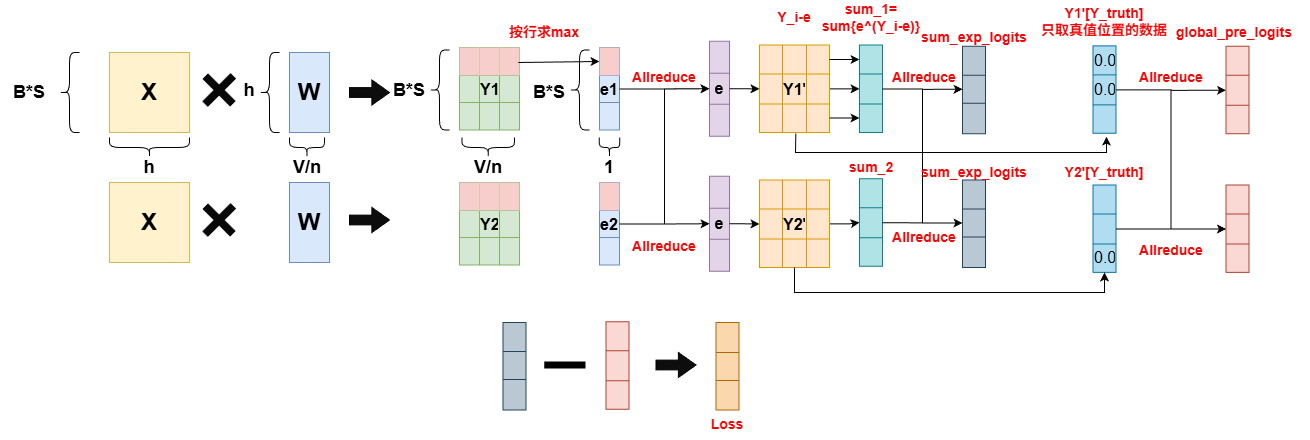
megatron对于CrossEntoryLoss的求解过程如上图所示,步骤不太一样,但是其实最终效果和safe softmax求解出来的效果,在数学上是等价的。首先我们先来看一下,softmax的求解方法:
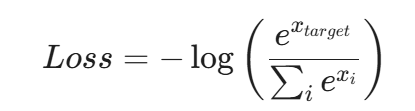
我们进行拆解:
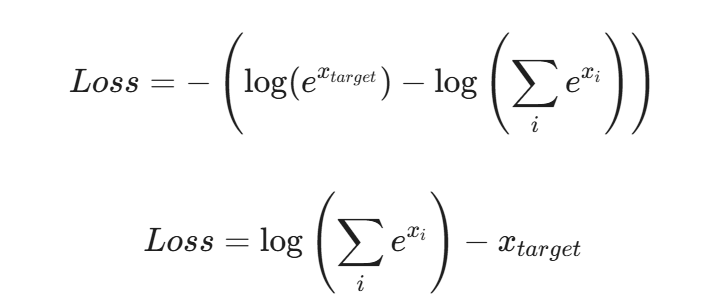
其实megatron实现的就是最后这个公式展现的一个差值。而为了放置数值的溢出,加入了safe softmax的处理,即每一项都减去这一组logits数据的最大值M,可以看到,其实是和原本的softmax是等价的,但是通过这个减法操作,可以有效地避免数值的溢出:
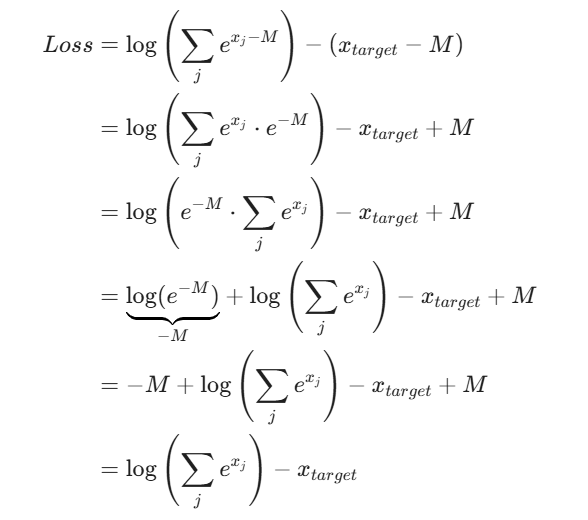
但是其实我们可以观察到,这样操作确实让每个tp_rank在计算loss 时,显存降低了,原来需要(B,S,V),现在降低到了N倍,但是这里会多增加两次allreduce的通信,因此算是时间换空间的操作。
3.流水并行实现细节
1.初始化Rank的处理的Layer
首先计算每个Rank需要处理的Layer数量,即使用get_num_layers_to_build函数(相关逻辑在 megatron/core/transformer/transformer_block.py 中):
def get_num_layers_to_build(config: TransformerConfig) -> int:
"""
确定当前流水线阶段需要构建的 Transformer 层的数量
"""
# 检查是否配置了首尾阶段的不均匀层数分配
if config.first_pipeline_num_layers is not None or config.last_pipeline_num_layers is not None:
assert (
parallel_state.get_virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_world_size() is None
), "不均匀层分配与交错流水线调度不兼容"
# 剩余的层数需要在其他流水线阶段中分配
layers_to_distribute = config.num_layers
# 计算剩余的流水线阶段数量
pipeline_stages_left = parallel_state.get_pipeline_model_parallel_world_size()
# 如果配置了首阶段层数,优先分配到第一阶段
if config.first_pipeline_num_layers is not None:
layers_to_distribute -= config.first_pipeline_num_layers
pipeline_stages_left -= 1
# 如果当前是第一阶段,直接返回层数
if parallel_state.is_pipeline_first_stage():
return config.first_pipeline_num_layers
# 如果配置了尾阶段层数,优先分配到最后阶段
if config.last_pipeline_num_layers is not None:
layers_to_distribute -= config.last_pipeline_num_layers
pipeline_stages_left -= 1
# 如果当前是最后阶段,直接返回层数
if parallel_state.is_pipeline_last_stage():
return config.last_pipeline_num_layers
# 确保剩余的层数可以均匀分配到剩余的流水线阶段中
assert (
layers_to_distribute % pipeline_stages_left == 0
), "剩余层数必须能被剩余的流水线阶段整除"
# 计算每个阶段分配的层数
num_layers_per_pipeline_rank = layers_to_distribute // pipeline_stages_left
else:
# 均匀分配的情况:每个流水线阶段平均分配层数
pipeline_ranks = config.pipeline_model_parallel_size
num_layers_per_pipeline_rank = config.num_layers // pipeline_ranks
# 检查是否使用了虚拟流水线并行(交错流水线分配)
if parallel_state.get_virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_world_size() is not None:
# 交错流水线并行:
# 每个流水线阶段的层数进一步被虚拟流水线切分
vp_size = parallel_state.get_virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_world_size()
num_layers_per_virtual_rank = num_layers_per_pipeline_rank // vp_size
num_layers_to_build = num_layers_per_virtual_rank
else:
# 非交错流水线并行:
# 每个阶段分配一组连续的层
num_layers_to_build = num_layers_per_pipeline_rank
# 返回当前流水线阶段实际需要构建的层数
return num_layers_to_build
因为中间层都是同样的Block,但是模型的输入输出层还有一些特殊的处理,因此第一个块和最后一个块的layer层要做�一些特殊处理,而剩余的layer则均分给中间的每一个rank。
获取到每个rank需要处理的Layer数后,在构建Transformer模型时,可以根据这个数量来创建当前rank需要处理的Layer,即使用_get_block_submodules函数:
def _get_block_submodules(
config: TransformerConfig, spec: Union[TransformerBlockSubmodules, ModuleSpec]
):
...
elif isinstance(spec, ModuleSpec):
if issubclass(spec.module, TransformerBlock):
return spec.submodules
elif issubclass(spec.module, BaseTransformerLayer):
num_layers = get_num_layers_to_build(config)
return TransformerBlockSubmodules(
layer_specs=[spec] * num_layers, layer_norm=LayerNormImpl
)
else:
raise Exception(f"specialize for {spec.module.__name__}.")
else:
raise Exception(f"specialize for {type(spec).__name__}.")
2.流水并行入口函数
def get_forward_backward_func():
pipeline_model_parallel_size = parallel_state.get_pipeline_model_parallel_world_size()
if pipeline_model_parallel_size > 1:
if parallel_state.get_virtual_pipeline_model_parallel_world_size() is not None:
return forward_backward_pipelining_with_interleaving
else:
return forward_backward_pipelining_without_interleaving
else:
return forward_backward_no_pipelining
分别forward_backward_pipelining_with_interleaving和forward_backward_pipelining_without_interleaving对应VPP和1F1B。
# 获取当前流水线的模型层类型和通信的张量形状
model_type = get_model_type(model)
encoder_decoder_xattn = get_model_xattn(model)
rank = parallel_state.get_pipeline_model_parallel_rank()
recv_tensor_shapes = get_tensor_shapes(
rank=rank - 1,
model_type=model_type,
seq_length=seq_length,
micro_batch_size=micro_batch_size,
decoder_seq_length=decoder_seq_length,
config=config,
encoder_decoder_xattn=encoder_decoder_xattn,
)
send_tensor_shapes = get_tensor_shapes(
rank=rank,
model_type=model_type,
seq_length=seq_length,
micro_batch_size=micro_batch_size,
decoder_seq_length=decoder_seq_length,
config=config,
encoder_decoder_xattn=encoder_decoder_xattn,
)
由于每个rank要从其它rank接收和发送数据,因此需要使用get_tensor_shapes函数,根据当前Rank所在的流水线阶段和模型结构,计算需要传输的张量形状。
3.释放内存机制
def deallocate_output_tensor(out, deallocate_pipeline_outputs=False):
'''伪内存释放(pseudo-deallocate):将输出张量的 '.data' 字段重置为标量张量。
这个方法应该在输出张量发送到下一个流水线阶段后立即调用。
在这个时刻,输出张量只需要保留 '.grad_fn' 字段,用于反向传播。
它的 '.data' 字段则可以安全释放以节省显存。
'''
if (out is None) or (not deallocate_pipeline_outputs):
# 如果输出张量为空,或者没有开启显存释放选项,直接返回。
return
# 确保输出是一个 torch.Tensor 对象
assert isinstance(out, torch.Tensor), f"预期是 Tensor 类型,但收到 {type(out).__name__} 类型"
# 确保释放的张量不是另一个张量的视图,否则释放会导致基础张量也受到影响
assert out._base is None, "不能释放基于其他张量创建的视图张量。"
# 将张量的 `.data` 字段设置为一个大小为 1 的标量张量,伪释放显存
out.data = torch.empty((1,), device=out.device, dtype=out.dtype)
流水线并行中,每个阶段会产生大量的中间张量,比如forward过程中,当前stage发送activation值给下一个stage,此时这个值会用在下一个stage的forward过程以及backward过程,所以当前stage存储的这个值就可以丢掉了,但是不能直接删除,因为这会导致计算图断裂,backward的时候找不到链式路线。因此这里使用的伪内存释放,即若当前张量不被其它变量引用,则直接将该张量的大小重置为大小为1的标量,释放原来的内存,但该张量仍保留,而不是像真正释放内存那样,直接删除该张量。
4.cooldown阶段的梯度同步
# 处理剩余的梯度同步操作,确保所有设备间的梯度都正确同步。
if no_sync_context is not None: # 如果存在未完成的同步上下文,开启同步。
enable_grad_sync()
if config.grad_sync_func is not None:
# 如果定义了自定义的梯度同步函数,调用它以同步所有模型参数的梯度。
config.grad_sync_func(model.parameters())
仅在最后一个micro_batch计算完后进行梯度同步,原因是,micro_batch之间的梯度是进行梯度累加的,而不是每一个micro_batch的数据都做一个参数更新,这样会造成数据噪声大、通信成本大,所以仅在最后一步backward做完后进行梯度同步,从而确保�:
1.所有 GPU 上的局部梯度都正确同步并合并,特别是对于数据并行和流水并行混合的场景,数据并行的模型块之间的梯度要做同步;
2.跨设备共享的参数梯度也需要进行同步,比如输入层用的embedding层和输出层用的lm_head层共享参数,也需要在此时同步梯度。
5.流水线并行中的通信机制
其核心通信函数即_communicate,而recv_forward,send_backward,send_forward_recv_backward等等函数都是对该函数的封装,因此这里主要探讨这个基础函数。
5.1 通信前的准备操作
# 初始化用于接收来自前后阶段的张量的函数
tensor_recv_prev_func = None
tensor_recv_next_func = None
# 如果不是变量长度序列,则接收前后阶段的形状与传入的 tensor_shape 相同
if not config.variable_seq_lengths:
recv_prev_shape = tensor_shape
recv_next_shape = tensor_shape
else:
# 如果序列长度是变量长度,则先进行形状协商
recv_prev_shape, recv_next_shape = _communicate_shapes(
tensor_send_next, tensor_send_prev, recv_prev, recv_next, config
)
# 定义创建接收张量的函数(前一个阶段的张量)
def create_tensor_recv_prev():
return torch.empty(
recv_prev_shape,
requires_grad=True,
device=torch.cuda.current_device(),
dtype=config.pipeline_dtype, # 使用 pipeline dtype
)
# 定义创建接收张量的函数(下一个阶段的张量)
def create_tensor_recv_next():
return torch.empty(
recv_next_shape,
requires_grad=True,
device=torch.cuda.current_device(),
dtype=config.pipeline_dtype, # 使用 pipeline dtype
)
# 如果需要从前一个阶段接收数据,设置接收张量的函数
if recv_prev:
if config.pipeline_dtype is None:
raise RuntimeError("pipeline_dtype must be provided if recv_prev is True")
if tensor_shape is None:
raise RuntimeError("tensor_shape must be specified if recv_prev is True.")
tensor_recv_prev_func = create_tensor_recv_prev # 将创建张量的函数指向前一个阶段的接收函数
# 如果需要从下一个阶段接收数据,设置接收张量的函数
if recv_next:
if config.pipeline_dtype is None:
raise RuntimeError("dtype must be provided if recv_next is True")
if tensor_shape is None:
raise RuntimeError("tensor_shape must be specified if recv_next is True.")
tensor_recv_next_func = create_tensor_recv_next # 将创建张量的函数指向下一个阶段的接收函数
# 根据配置选择通信方法
if config.use_ring_exchange_p2p:
# 如果使用环形交换通信
def _ring_exchange_wrapper(**kwargs):
torch.distributed.ring_exchange(**kwargs) # 使用环形交换进行数据传输
return []
p2p_func = _ring_exchange_wrapper # 设置为环形交换函数
elif config.batch_p2p_comm:
# 如果使用批量点对点通信
assert wait_on_reqs
p2p_func = _batched_p2p_ops # 设置为批量点对点通信操作函数
else:
# 默认使用常规点对点通信
p2p_func = _p2p_ops
首先判断是否为变长序列,如果是,需要进行形状协商,从而得到每一步需要接受的数据大小,为了接收next_rank和pre_rank的数据,需要创建对应大小的缓冲区,这里用torch.empty进行创建,如果需要接收,则接受张量函数就是创建缓冲区的函数。最后选择通信方式。
5.2 通信过程
# 获取当前 pipeline 中的分组信息(例如,不同的阶段之间的组别、前后设备的 rank)
pp_group = get_pipeline_model_parallel_group()
next_rank = get_pipeline_model_parallel_next_rank()
prev_rank = get_pipeline_model_parallel_prev_rank()
# 如果并行组只有一个元素,将其转为列表以简化后续处理
if not isinstance(pp_group, list):
pp_group = [pp_group]
next_rank = [next_rank]
prev_rank = [prev_rank]
# 初始化请求列表,用于存储通信请求
reqs = [] if config.use_ring_exchange_p2p or config.batch_p2p_comm else {}
# 初始化请求列表,用于存储通信请求
reqs = [] if config.use_ring_exchange_p2p or config.batch_p2p_comm else {}
# 用于存储接收到的张量(来自前后阶段)
tensor_recv_prev_list = []
tensor_recv_next_list = []
# 遍历每个管道组及其对应的 rank,执行数据传输
for group, nr, pr in zip(pp_group, next_rank, prev_rank):
# 如果需要接收来自前一个阶段的数据,则创建接收张量
if tensor_recv_prev_func is not None:
tensor_recv_prev = tensor_recv_prev_func()
tensor_recv_prev_list.append(tensor_recv_prev)
else:
tensor_recv_prev = None
# 如果需要接收来自下一个阶段的数据,则创建接收张量
if tensor_recv_next_func is not None:
tensor_recv_next = tensor_recv_next_func()
tensor_recv_next_list.append(tensor_recv_next)
else:
tensor_recv_next = None
# 调用通信函数进行数据传输
p2p_reqs = p2p_func(
tensor_send_prev=tensor_send_prev,
tensor_recv_prev=tensor_recv_prev,
tensor_send_next=tensor_send_next,
tensor_recv_next=tensor_recv_next,
group=group,
prev_pipeline_rank=pr,
next_pipeline_rank=nr,
)
# 如果是多个请求,追加到请求列表中
if isinstance(p2p_reqs, list):
reqs.extend(p2p_reqs)
else:
reqs.update(p2p_reqs)
获取PP通信组,以及相邻的前后rank。遍��历如果需要接收数据,则创建缓冲区,并且用p2p_func创建通信任务,可以是_p2p_ops点对点通信、_batched_p2p_ops批量点对点通信 或 _ring_exchange_wrapper环状p2p通信等通信方式。
5.3 奇数偶数通信策略
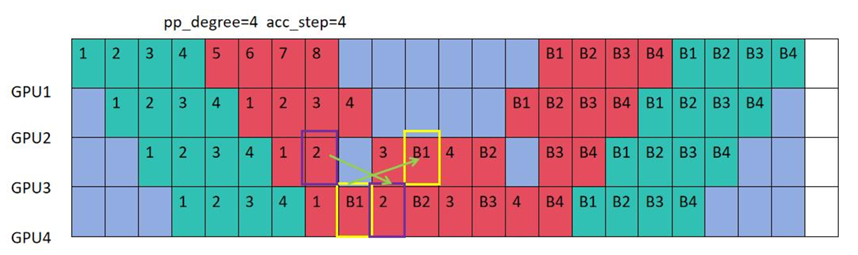
我们注意到,普通的1F1B,VPP在Steady阶段会出现hang住的问题,如图GPU3向GPU4发送forward的数据,GPU4也向GPU3发送backward的数据,这时候就会hang住。
我们来分析一下为什么?
首先需要明确一点,isend是需要占用通信资源来发送数据,而irecv虽然也是通信,用于接收数据,但是从上面就能看出来,它并不需要调用通信资源去实际处理数据,而是在本地创建一个缓冲区,等待其它rank给它发送数据,同时isend和irecv是异步操作,所以本身并不会造成进程阻塞。
但是我们需要注意,在每个 rank 上,NCCL 的 send 和 recv 通信操作通常被顺序地 enqueue 到同一个通信 stream 中。由于 CUDA stream 是严格顺序执行的,如果两个 rank 都先 enqueue send,再 enqueue recv,那么在执行 send kernel 时,对端的 recv kernel 尚未获得执行机会。此时 send kernel 会等待对端 recv 就绪,而 recv kernel 又被排在 send 之后,无法启动,从而在两个 rank 之间形成循环等待,最终导致通信 hang。
奇偶通信通过错开 send/recv 的 enqueue 顺序,保证至少一端的 recv 能先执行,从�而避免该死锁。
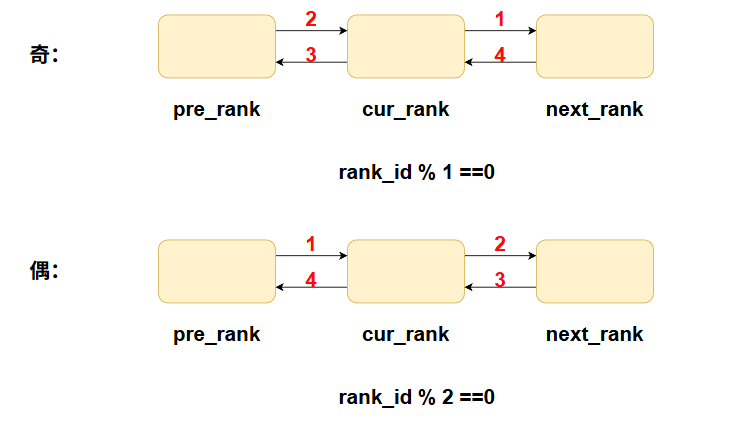
即每个rank在一个通信stream里根据rank_id的奇偶性顺序添加通信操作(代码具体会判断是否为None,为None则不需要添加通信):
def _p2p_ops(...):
if rank % 2 == 0:
# 偶数Rank顺序:发送→接收→发送→接收
isend(next_rank) → irecv(prev_rank) → isend(prev_rank) → irecv(next_rank)
else:
# 奇数Rank顺序:接收→发送→接收→发送
irecv(prev_rank) → isend(next_rank) → irecv(next_rank) → isend(prev_rank)
其实出现hang住的地方主要是在1F1B阶段,因此其实可以直接将recv_forward,send_backward拆解出来,所有1F1B阶段都遵循:
recv_backward->计算backward->recv_forward->send_backward->计算forward->send_forward
即可。
4.混合精度训练
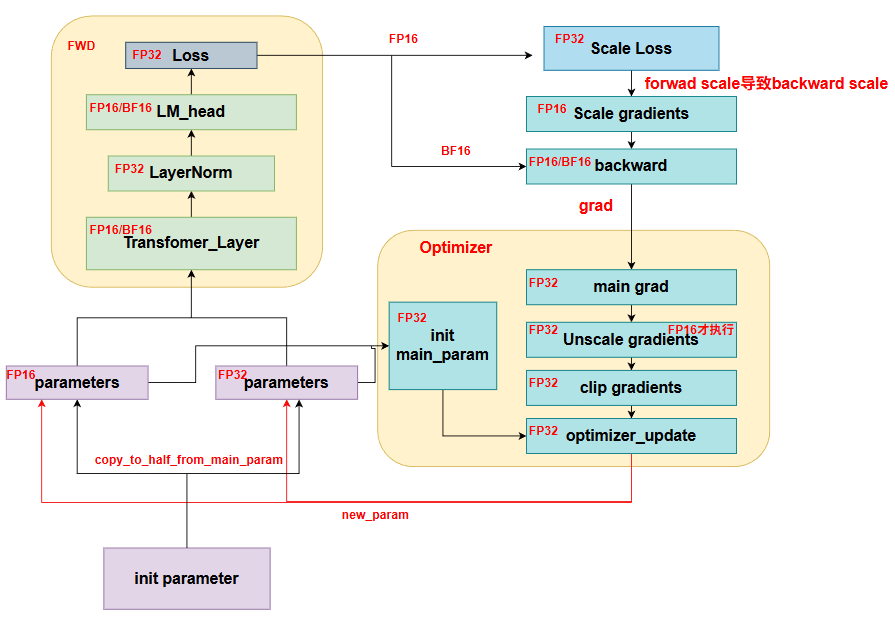
如图所示为混合精度训练的一些流程,主要有以下几点需要注意:
1.在forward和backward过程中,除了一些特殊的层如:LayerNorm,selfattention的softmax,RoPE,部分激活函数以及Loss是FP32,其它均为FP16.
2.main_param仅用于做参数更新,因此在创建时,需要和计算图断开,防止梯度传播。
3.初始化的时候,可以根据需要,将各个参数按dtype进行初始化。
4.scale loss的目的是防止FP16精度下,精度下溢,因此FP16相对于FP32和BF16来说,数值范围更小,会出现精度下溢的现象,需要乘以一个放缩因子,进行放大。相应的在backward的时候,对应grad也因此增大了。在进入optimizer之后,需要将model_grad转换成main_grad,即从FP16/BF16转换成FP32,然后因为之前做了scale,因此这里需要做unscale恢复为原来的数据,因为此时在FP32下,因此相对于FP16来说,不会出现精度下溢,并且为了确保数据准确性需要恢复。紧接着对grad做clip,对于Global Norm而言:使用L2范数,即对于每个grad算一个L2范数,然后再算平方和,再开放,相当于对所有grad的全部元素算L2范数,如下:
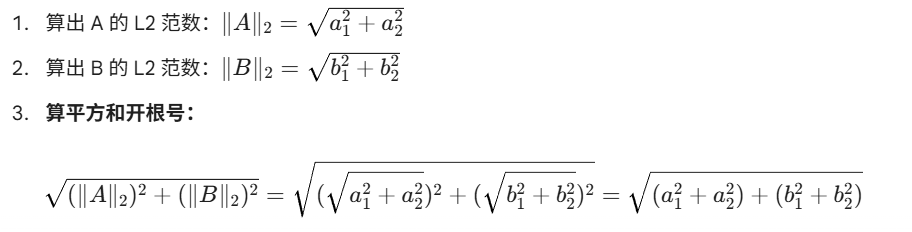
接着如果算出来的Global Norm大于阈值c,则每一个需要clip的grad,都乘以,进行梯度裁剪。
动态损失放大(DynamicGradScaler)
class MegatronGradScaler(ABC):
def __init__(self, initial_scale):
"""Initialize scale value with the input initial scale.
初始化loss_scale,同时规定loss_scale必须大于0
"""
assert initial_scale > 0.0
self._scale = torch.cuda.FloatTensor([initial_scale])
@property
def scale(self):
return self._scale
@property
def inv_scale(self):
return self._scale.double().reciprocal().float()
@abstractmethod
def update(self, found_inf):
pass
@abstractmethod
def state_dict(self):
pass
@abstractmethod
def load_state_dict(self, state_dict):
pass
class DynamicGradScaler(MegatronGradScaler):
def __init__(
self,
initial_scale,
min_scale,
growth_factor,
backoff_factor,
growth_interval,
hysteresis,
):
""" "Grad scaler with dynamic scale that gets adjusted
during training.
Params:
self._scale:表示初始化loss scale
self.min_scale:表示loss scale的最小值
self.growth_interval:表示连续无梯度上溢的迭代次数
self.growth_factor:当连续self.growth_interval次未出现梯度上溢时,
就将loss scale扩大self.growth_factor倍
self.hysteresis:表示最多允许出现梯度上溢的迭代次数
self.backoff_factor:当累计出现self.hysteresis次梯度上溢的情况时(注意是累计不是连续),
则将loss scale缩小self.backoff_factor倍。
缩小公式为self._scale = torch.max(self._scale * self.backoff_factor, self.min_scale)。
缩小后重新开始计算梯度上溢的次数。
"""
super(DynamicGradScaler, self).__init__(initial_scale)
# Lower bound on the scale.
assert min_scale > 0.0
assert min_scale <= initial_scale
self.min_scale = torch.cuda.FloatTensor([min_scale])
# Growth and backoff factors for the scale.
assert growth_factor > 1.0
self.growth_factor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor([growth_factor])
assert backoff_factor < 1.0
assert backoff_factor > 0.0
self.backoff_factor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor([backoff_factor])
# Interval over which if we don't see any inf/nan,
# we will scale the grad scale by the growth factor.
assert growth_interval > 0
self.growth_interval = growth_interval
# Number of inf/nans we should see before scaling down
# the grad scale by the backoff factor.
assert hysteresis > 0
self.hysteresis = hysteresis
# Trackers.
self._growth_tracker = 0
self._hysteresis_tracker = self.hysteresis
def update(self, found_inf):
"""
更新loss scale
"""
# -------------------------------------------------------------
# 一旦发现梯度溢出(inf/nan)的情况
# -------------------------------------------------------------
if found_inf:
self._growth_tracker = 0
self._hysteresis_tracker -= 1
# 如果_hysteresis_tracker变成<=0了,
# 说明梯度溢出的次数已经超过了我们设定的阈值,
# 这时就要惩罚性地缩小loss_scale
我们就要减少loss_scale
if self._hysteresis_tracker <= 0:
self._scale = torch.max(
self._scale * self.backoff_factor, self.min_scale
)
# -------------------------------------------------------------
# 如果没有发现梯度inf/nan
# -------------------------------------------------------------
else:
# If there is no nan/inf, increment the growth tracker.
self._growth_tracker += 1
# 如果我们已经连续多次没有出现inf/nan,我们就可以增大loss scale
if self._growth_tracker == self.growth_interval:
# Reset the tracker and hysteresis trackers,
self._growth_tracker = 0
self._hysteresis_tracker = self.hysteresis
# and scale up the loss scale.
self._scale = self._scale * self.growth_factor
def state_dict(self):
state_dict = {}
state_dict["scale"] = self._scale
state_dict["growth_tracker"] = self._growth_tracker
state_dict["hysteresis_tracker"] = self._hysteresis_tracker
return state_dict
def load_state_dict(self, state_dict):
self._scale = state_dict["scale"].cuda(torch.cuda.current_device())
self._growth_tracker = state_dict["growth_tracker"]
self._hysteresis_tracker = state_dict["hysteresis_tracker"]
主要思想就是,如果当前scale后,没有出现上溢,就做scale,否则放弃这次更新,并且,如果_hysteresis_tracker<0说明上溢次数超过了设定的阈值,则要缩小scale,即除以self.growth_factor,相应的,如果没有出现上溢并且做了scale达到一定次数,此时可以增大loss scale,即乘以self.growth_factor。
混合精度训练实现(Float16OptimizerWithFloat16Params)
class Float16OptimizerWithFloat16Params(MegatronOptimizer):
"""Float16 optimizer for fp16 and bf16 data types.
Arguments:
optimizer: base optimizer such as Adam or SGD
clip_grad: clip gradeints with this global L2 norm. Note
that clipping is ignored if clip_grad == 0
梯度剪裁的阈值(也就是3.4中说的常量c),如果等于0说明我们不做梯度剪裁
log_num_zeros_in_grad: return number of zeros in the gradients.
params_have_main_grad: flag indicating if parameters have
a `main_grad` field. If this is set, we are assuming
that the model parameters are store in the `main_grad`
field instead of the typical `grad` field. This happens
for the DDP cases where there is a contihuous buffer
holding the gradients. For example for bfloat16, we want
to do gradient accumulation and all-reduces in float32
and as a result we store those gradients in the main_grad.
Note that main grad is not necessarily in float32.
相关说明见4.1中的解释,注意main_grad并不一定是fp32的
bf16: if true, the model is running in bfloat16.
grad_scaler: used for scaling gradients. Note that this can be
None. This case happens when `bf16 = True` and we don't
use any loss scale. Note that for `bf16 = True`, we can have
a constnat gradient scaler. Also for `bf16 = False`, we
always require a grad scaler.
当模型是用bf16跑的时候,我们要么用一个常数的loss scale,要么不用loss scale(原因见3.3(1)),
不用的话grad_scaler = None
当模型不是bf16跑的时候,我们一般要用一个loss scale,至于是常数的,还是动态的,就靠自己决定了
"""
def __init__(
self,
optimizer,
clip_grad,
log_num_zeros_in_grad,
params_have_main_grad,
bf16,
grad_scaler,
):
super(Float16OptimizerWithFloat16Params, self).__init__(
optimizer, clip_grad, log_num_zeros_in_grad, params_have_main_grad
)
self.bf16 = bf16
self.grad_scaler = grad_scaler
# -------------------------------------------------------------------
# None grad scaler is only supported for bf16.
# 用fp16跑模型时,一定要用loss scale
# -------------------------------------------------------------------
if self.grad_scaler is None:
assert self.bf16, "fp16 expects a grad scaler."
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Tensor used to determine if a nan/if has happend.
# Any non-zero value indicates inf/nan.
# Note that we keep this for the cases that grad scaler is none.
# We still record nan/inf if we have a bfloat16 with a grad scaler.
# 用于记录【所有gpu上】是否发生了梯度溢出的情况,
# 值为0时表示所有gpu上都没有梯度溢出情况;值不为0时表示至少1块gpu上出现梯度溢出情况
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
if self.grad_scaler:
self.found_inf = torch.cuda.FloatTensor([0.0])
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Dummy tensor needed for apex multi-apply tensor.
# For bfloat, we don't have multi-tensor apply and for now
# we set it to none so the multi-tensor apply gets ignored.
# 这是在定义apex的multi_tensor_applier函数的其中一个参数,
# 该函数的目的是在fp16的精度下让数据复制更有效率(在一个kernel内完成复制)
# bf16下还没有相关的优化操作。
# 如果不使用该函数,则正常用tensor.copy_(src)的方式做复制
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
if bf16:
self._dummy_overflow_buf = None
else:
self._dummy_overflow_buf = torch.cuda.IntTensor([0])
# In case grad scaler is not passed, define the unity scale.
if self.grad_scaler is None:
self._scale_one = torch.cuda.FloatTensor([1.0])
# ======================
# main parameter stuff
# ======================
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Three groups of parameters:
# float16_groups: original float16 parameters
# fp32_from_float16_groups: fp32 copy of float16 parameters
# fp32_from_fp32_groups: original fp32 parameters
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
self.float16_groups = [] # 装原始就是fp16/bf16的权重
self.fp32_from_float16_groups = [] # 装从fp16拷贝并转换而来的fp32权重
self.fp32_from_fp32_groups = [] # 装原始就是fp32的权重
# For all the groups in the original optimizer:
for param_group in self.optimizer.param_groups:
float16_params_this_group = []
fp32_params_this_group = []
fp32_from_float16_params_this_group = []
# For all the parameters in this group:
for i, param in enumerate(param_group["params"]):
if param.requires_grad:
# float16 params:
if param.type() in [
"torch.cuda.HalfTensor",
"torch.cuda.BFloat16Tensor",
]:
# 原始就是fp16/bf16的权重
float16_params_this_group.append(param)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Create a copy
# 将原始就是fp16/bf16的权重转变为fp32的形式
# detach:新的权重脱离了计算图(requires_grad = False),但是和旧权重共享内存
# clone:开辟了新的内存
# float:转成fp32
# 最终实现:从fp16/bf16转成fp32,同时脱离计算图,同时开辟新内存的目的。
# 单独用detach无法开辟新内存,单独用clone无法脱离计算图
# ref:https://blog.csdn.net/winycg/article/details/100813519
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
main_param = param.detach().clone().float()
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Copy tensor model parallel attributes.
# 将tp并行相关的tensor属性拷贝到这些转换而来的fp32上
# 对此有疑惑的,可以参考Megatron源码解读第一篇:分布式环境初始化
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
mpu.copy_tensor_model_parallel_attributes(main_param, param)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# 另外,将是否是输出层WE的情况拷贝到转换而来的fp32上
#(复习一下,shared这个属性只在pp度非0时的输出层WE才有)
# 参考Megatron源码解读第二篇:模型并行,Word Embedding相关代码
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
if hasattr(param, "shared"):
main_param.shared = param.shared
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Replace the optimizer params with the new fp32 copy.
# 将optimizer中的参数用fp32代替
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
param_group["params"][i] = main_param
fp32_from_float16_params_this_group.append(main_param)
# Reset existing state dict key to the new main param.
if param in self.optimizer.state:
self.optimizer.state[main_param] = self.optimizer.state.pop(
param
)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# fp32 params.
# 原始是fp32的权重
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
elif param.type() == "torch.cuda.FloatTensor":
fp32_params_this_group.append(param)
param_group["params"][i] = param
else:
raise TypeError(
"Wrapped parameters must be one of "
"torch.cuda.FloatTensor, "
"torch.cuda.HalfTensor, or "
"torch.cuda.BFloat16Tensor. "
"Received {}".format(param.type())
)
self.float16_groups.append(float16_params_this_group)
self.fp32_from_float16_groups.append(fp32_from_float16_params_this_group)
self.fp32_from_fp32_groups.append(fp32_params_this_group)
# Leverage state_dict() and load_state_dict() to
# recast preexisting per-param state tensors
self.optimizer.load_state_dict(self.optimizer.state_dict())
def zero_grad(self, set_to_none=True):
"""We only need to zero the model related parameters, i.e.,
float16_groups & fp32_from_fp32_groups.
我们只对参与模型训练的那部分参数做梯度计算(同理做梯度清0),
对optimizer中存储的fp32的states不做梯度计算/清理处理,这部分states只用于做更新
"""
for group in self.float16_groups:
_zero_grad_group_helper(group, set_to_none)
for group in self.fp32_from_fp32_groups:
_zero_grad_group_helper(group, set_to_none)
def get_loss_scale(self):
if self.grad_scaler is None:
return self._scale_one
return self.grad_scaler.scale
def _copy_model_grads_to_main_grads(self):
"""
将model grads拷贝到main grads上去
"""
# This only needs to be done for the float16 group.
for model_group, main_group in zip(
self.float16_groups, self.fp32_from_float16_groups
):
for model_param, main_param in zip(model_group, main_group):
if self.params_have_main_grad: # 相关定义见4.1
# 将梯度从fp16转为fp32
main_param.grad = model_param.main_grad.float()
else:
if model_param.grad is not None:
main_param.grad = model_param.grad.float()
# For fp32 grads, we need to reset the grads to main grad.
if self.params_have_main_grad:
for model_group in self.fp32_from_fp32_groups:
for model_param in model_group:
model_param.grad = model_param.main_grad
def _unscale_main_grads_and_check_for_nan(self):
main_grads = []
# fp32 params fromm float16 ones.
for main_group in self.fp32_from_float16_groups:
for main_param in main_group:
if main_param.grad is not None:
main_grads.append(main_param.grad.data)
# Append fp32 parameters.
for main_group in self.fp32_from_fp32_groups:
for main_param in main_group:
if main_param.grad is not None:
main_grads.append(main_param.grad.data)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Reset found inf.
# 用于记录全局(所有的gpu上)是否存在梯度溢出的情况
# self.found_inf为0,则不存在梯度溢出;否则至少1块gpu存在梯度溢出情况
# 如果存在梯度溢出,将会跳过该轮step()更新
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
self.found_inf.fill_(0.0)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Unscale and set found inf/nan
# 这里做两件事:
# 1、判断scale后是否存在梯度溢出
# 2、unscale梯度,将梯度恢复正常值,为更新做准备
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
torch._amp_foreach_non_finite_check_and_unscale_(
main_grads, self.found_inf, self.grad_scaler.inv_scale
)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Update across all model parallel instances.
# 检查全局上是否有梯度溢出情况
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
torch.distributed.all_reduce(
self.found_inf,
op=torch.distributed.ReduceOp.MAX,
group=mpu.get_model_parallel_group(),
)
# Check for nan.
found_inf_flag = self.found_inf.item() > 0
return found_inf_flag
def _get_model_and_main_params_data_float16(self):
"""
得到原始fp16的权重和由fp16转变而来的fp32的权重
"""
model_data = []
main_data = []
for model_group, main_group in zip(
self.float16_groups, self.fp32_from_float16_groups
):
for model_param, main_param in zip(model_group, main_group):
model_data.append(model_param.data)
main_data.append(main_param.data)
return model_data, main_data
def _copy_main_params_to_model_params(self):
# Only needed for the float16 params.
model_data, main_data = self._get_model_and_main_params_data_float16()
_multi_tensor_copy_this_to_that(
this=main_data, that=model_data, overflow_buf=self._dummy_overflow_buf
)
def _copy_model_params_to_main_params(self):
# Only needed for the float16 params.
model_data, main_data = self._get_model_and_main_params_data_float16()
_multi_tensor_copy_this_to_that(
this=model_data, that=main_data, overflow_buf=self._dummy_overflow_buf
)
def reload_model_params(self):
self._copy_model_params_to_main_params()
@torch.no_grad()
def step(self):
"""
重写optimizer中的step()操作,也就是用梯度更新权重这一部分
"""
timers = get_timers()
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Copy gradients from model params to main params.
# 1、首先,把model grads转变成fp32的形式,并拷贝到main_grads上
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
timers("optimizer-copy-to-main-grad").start()
self._copy_model_grads_to_main_grads()
timers("optimizer-copy-to-main-grad").stop()
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Do unscale, check for inf, and update grad scaler only for
# the case that grad scaler is provided.
# 2、如果我们做过loss scale
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
if self.grad_scaler:
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Unscale and check for inf/nan.
# 遍历【每块】GPU,检查是否存在梯度溢出情况,并将main_grads还原成未scale的值
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
timers("optimizer-unscale-and-check-inf").start()
found_inf_flag = self._unscale_main_grads_and_check_for_nan()
timers("optimizer-unscale-and-check-inf").stop()
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# We are done with scaling gradients
# so we can update the loss scale.
# 根据溢出的检查结果,动量更新loss scale,原理见3.3(3)
# 如果是常数scaler,则update后scale不变;
# 如果是动态scaler,则会根据scale前梯度是否存在nan/inf来动态调整scale的大小
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
self.grad_scaler.update(found_inf_flag)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# If we found inf/nan, skip the update.
# 一旦存在梯度nan/inf的情况,则跳过这个step,不做权重更新
# return的三个值分别表示:是否更新成功,clip中的total_norm(见3.4),值为0的梯度数
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
if found_inf_flag:
return False, None, None
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Clip the main gradients.
# 3、梯度剪裁
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
timers("optimizer-clip-main-grad").start()
grad_norm = None
if self.clip_grad > 0.0:
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# 这是对main grad做inplace的剪裁,grad_norm返回的是total_norm
# clip_grad_norm的实现就不细讲啦,大家自己看代码细节即可
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
grad_norm = self.clip_grad_norm(self.clip_grad)
timers("optimizer-clip-main-grad").stop()
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# count the zeros in the grads
# 4、统计为0的梯度数
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
num_zeros_in_grad = self.count_zeros() if self.log_num_zeros_in_grad else None
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Step the optimizer.
# 5、正常更新optimizer,
# 由于我们在__init__中就将optimizer的param从fp16指向了fp32,
# 所以这里更新的是fp32(main_param)的结果
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
self.optimizer.step()
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Update params from main params.
# 6、将main_param拷贝给model_param
# 有了更�新完的fp32权重,就能做下一轮训练了,所以这时我们需要用新的fp32权重
# 去更新一次fp16权重
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
timers("optimizer-copy-main-to-model-params").start()
self._copy_main_params_to_model_params()
timers("optimizer-copy-main-to-model-params").stop()
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
# Successful update.
# 是否成功update、total_norm,值为0的梯度个数
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------
return True, grad_norm, num_zeros_in_grad
def state_dict(self):
state_dict = {}
state_dict["optimizer"] = self.optimizer.state_dict()
if self.grad_scaler:
state_dict["grad_scaler"] = self.grad_scaler.state_dict()
state_dict["fp32_from_fp16_params"] = self.fp32_from_float16_groups
return state_dict
def load_state_dict(self, state_dict):
# Optimizer.
optimizer_key = "optimizer"
if optimizer_key not in state_dict:
optimizer_key = "optimizer_state_dict"
print_rank_0(
"***WARNING*** loading optimizer from " "an old checkpoint ..."
)
self.optimizer.load_state_dict(state_dict[optimizer_key])
# Grad scaler.
if "grad_scaler" not in state_dict:
print_rank_0(
"***WARNING*** found an old checkpoint, will not "
"load grad scaler ..."
)
else:
if self.grad_scaler:
self.grad_scaler.load_state_dict(state_dict["grad_scaler"])
else:
print_rank_0(
"***WARNING*** fould the grad scaler in the "
"checkpoint but it is None in the class. "
"Skipping loading grad scaler ..."
)
# Copy data for the main params.
fp32_from_float16_params_key = "fp32_from_fp16_params"
if fp32_from_float16_params_key not in state_dict:
fp32_from_float16_params_key = "fp32_from_fp16"
for current_group, saved_group in zip(
self.fp32_from_float16_groups, state_dict[fp32_from_float16_params_key]
):
for current_param, saved_param in zip(current_group, saved_group):
current_param.data.copy_(saved_param.data)
这里主要注意的是main_param需要脱离计算图,同事loss scale后的溢出检查是在全部的rank上检查,只要有一个rank上出现精度溢出,则此轮更新就作废。